YLT-11, a novel PLK4 inhibitor, inhibits human breast cancer growth via inducing maladjusted centriole duplication and mitotic defect
- PMID: 30337519
- PMCID: PMC6194023
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-1071-2
YLT-11, a novel PLK4 inhibitor, inhibits human breast cancer growth via inducing maladjusted centriole duplication and mitotic defect
Abstract
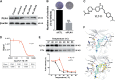
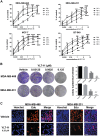
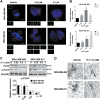
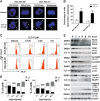
Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) is indispensable for precise control of centriole duplication. Abnormal expression of PLK4 has been reported in many human cancers, and inhibition of PLK4 activity results in their mitotic arrest and apoptosis. Therefore, PLK4 may be a valid therapeutic target for antitumor therapy. However, clinically available small-molecule inhibitors targeting PLK4 are deficient and their underlying mechanisms still remain not fully clear. Herein, the effects of YLT-11 on breast cancer cells and the associated mechanism were investigated. In vitro, YLT-11 exhibited significant antiproliferation activities against breast cancer cells. Meanwhile, cells treated with YLT-11 exhibited effects consistent with PLK4 kinase inhibition, including dysregulated centriole duplication and mitotic defects, sequentially making tumor cells more vulnerable to chemotherapy. Furthermore, YLT-11 could strongly regulate downstream factors of PLK4, which was involved in cell cycle regulation, ultimately inducing apoptosis of breast cancer cell. In vivo, oral administration of YLT-11 significantly suppressed the tumor growth in human breast cancer xenograft models at doses that are well tolerated. In summary, the preclinical data show that YLT-11 could be a promising candidate drug for breast tumor therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer
We claim that none of the materials in the paper has been published or is under consideration for publication elsewhere, all authors are aware of the submission and agree to its publication.
Figures
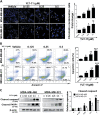
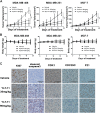
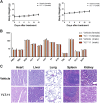
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

