Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
- PMID: 30337530
- PMCID: PMC6193978
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06475-9
Metallo-polyelectrolytes as a class of ionic macromolecules for functional materials
Abstract
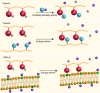
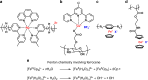
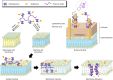
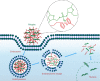
The fields of soft polymers and macromolecular sciences have enjoyed a unique combination of metals and organic frameworks in the name of metallopolymers or organometallic polymers. When metallopolymers carry charged groups, they form a class of metal-containing polyelectrolytes or metallo-polyelectrolytes. This review identifies the unique properties and functions of metallo-polyelectrolytes compared with conventional organo-polyelectrolytes, in the hope of shedding light on the formation of functional materials with intriguing applications and potential benefits. It concludes with a critical perspective on the challenges and hurdles for metallo-polyelectrolytes, especially experimental quantitative analysis and theoretical modeling of ionic binding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metallo-Polyelectrolytes: Correlating Macromolecular Architectures with Properties and Applications.Trends Chem. 2020 Mar;2(3):227-240. doi: 10.1016/j.trechm.2019.12.004. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Trends Chem. 2020. PMID: 34337370 Free PMC article.
-
From terpyridine-based assemblies to metallo-supramolecular polyelectrolytes (MEPEs).Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014 May;207:107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2013.12.010. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014. PMID: 24485594 Review.
-
Modulation of Properties through Covalent Bond Induced Formation of Strong Ion Pairing between Polyelectrolytes in Injectable Conetwork Hydrogels.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):3374-3387. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01673. Epub 2021 Mar 12. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2021. PMID: 35014422
-
Topologically frustrated dynamics of crowded charged macromolecules in charged hydrogels.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 8;9(1):2248. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04661-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29884894 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreconfigurable polymers for biomedical applications: chemistry and macromolecular engineering.Biomacromolecules. 2014 Oct 13;15(10):3474-94. doi: 10.1021/bm500990z. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Biomacromolecules. 2014. PMID: 25226507 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide as an In Situ Assistant in the Nucleation and Growth of Gold Nanoparticles.Materials (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;15(23):8557. doi: 10.3390/ma15238557. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500052 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial cobaltocenium copolymers: tuning amphiphilicity against NDM-1 bacteria.Biomater Sci. 2025 Jul 22;13(15):4232-4244. doi: 10.1039/d5bm00497g. Biomater Sci. 2025. PMID: 40559204 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Enzymatic Degradation, and Polymer-Miscibility Evaluation of Nonionic Antimicrobial Hyperbranched Polyesters with Indole or Isatin Functionalities.Biomacromolecules. 2021 May 10;22(5):2256-2271. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.1c00343. Epub 2021 Apr 26. Biomacromolecules. 2021. PMID: 33900740 Free PMC article.
-
Antifouling and antimicrobial cobaltocenium-containing metallopolymer double-network hydrogels.Biomater Transl. 2022 Jun 28;3(2):162-171. doi: 10.12336/biomatertransl.2022.02.008. eCollection 2022. Biomater Transl. 2022. PMID: 36105565 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in metallopolymer-based drug delivery systems.RSC Adv. 2019 Nov 13;9(63):37009-37051. doi: 10.1039/c9ra06678k. eCollection 2019 Nov 11. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35539076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hara, M. Polyelectrolytes: Science and Technology (CRC Press, 1992).
-
- Hiller JA, Mendelsohn JD, Rubner MF. Reversibly Erasable Nanoporous Anti-Reflection Coatings from Polyelectrolyte Multilayers. Nat. Mater. 2002;1:59–63. - PubMed
-
- Pack DW, Hoffman AS, Pun S, Stayton PS. Design and Development of Polymers for Gene Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2005;4:581–593. - PubMed
-
- Viovy JL. Electrophoresis of DNA and Other Polyelectrolytes: Physical Mechanisms. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2000;72:813.
-
- Dobrynin AV, Rubinstein M. Theory of Polyelectrolytes in Solutions and at Surfaces. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005;30:1049–1118.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

