Epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of Yunnan in southwestern China
- PMID: 30337598
- PMCID: PMC6194063
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-33816-x
Epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) of Yunnan in southwestern China
Abstract
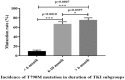
To explore the effect of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation status on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in Yunnan province of southwestern China. First, this study used the super amplification refractory mutation system (Super ARMS) polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Droplet Digital PCR (dd PCR) to evaluate the T790M gene mutation, in plasmatic ctDNA samples from 212 cases of NSCLC. The association between T790M mutations and clinical parameters were further explored. Next, to investigate the mechanism of drug resistance that resulted from T790M mutation, subgroup analyses according to duration of medicine (EGFR-TKIs) were carried out. Finally, we also evaluate the effectiveness of blood-based circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) on detecting the T790M mutation by calculating Super ARMS's detection efficiency. We found that the T790M mutation rate was 8.4% (18/212) in overall patients. The T790M mutation was more frequent in patients with brain metastasis 30.0% (12/40) (p < 0.01). We found that post-TKI samples 42.8% (15/35) were associated with a higher T790M mutation rate (p < 0.01). Subgroup analysis showed that the duration of TKI therapy for 6 to 10 months 66.6% (8/12) (p < 0.01) and >10 months 75.0% (9/12) (p < 0.01) were also associated with a higher T790M mutation rate. Super ARMS's sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy were 100.0%, 99.4%, 94.7%, 100.0%, and 99.5% respectively. Generally, the EGFR-T790M mutation was more common in NSCLC patients with brain metastasis and those who received TKI therapy for more than 6 months. Moreover, Super ARMS is a sensitive, efficient, and practical clinic method for dynamically monitoring T790M mutation status and effectively guiding clinic treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous