The effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, tadalafil, on in vitro potassium chloride-induced contractions of isolated human ureteral tissue
- PMID: 30337785
- PMCID: PMC6174708
- DOI: 10.4103/iju.IJU_107_18
The effect of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, tadalafil, on in vitro potassium chloride-induced contractions of isolated human ureteral tissue
Abstract
Introduction: Drugs causing ureteral relaxation are used for medical expulsive therapy (MET) for stones. We investigated the in vitro ability of tadalafil to cause relaxation of potassium chloride (KCl)-induced contractions of isolated human ureteral tissue.
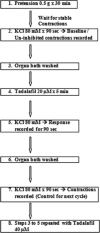
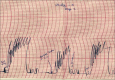
Materials and methods: Eight grossly normal proximal ureteral tissues were collected from the radical and donor nephrectomy specimen. The standard organ bath protocol was followed. Ureteral contractions were induced with 80 mM KCl before and after exposure to tadalafil.
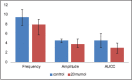
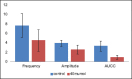
Results: The median amplitude and frequency of KCl-induced contractions and the median area under the contractility curve (AUCC) after exposure to 20 μM tadalafil showed significant reductions compared to that of before exposure to tadalafil (7.87 cm, 3.79/min, and 2.98 cm2, respectively, versus 9.37 cm, 4.48/min, and 4.50 cm2, respectively; P = 0,026, 0.008, and 0.008, respectively). After exposure to 40 μM tadalafil, the median amplitude and frequency of KCl-induced contractions and AUCC (4.50 cm, 2.56/min, and 0.92 cm2, respectively) showed significant reductions compared to that of before exposure to tadalafil (7.62 cm, 3.88/min, and 3.32 cm2, respectively; P = 0.008, 0.016, and 0.008, respectively). However, reductions in the parameters after exposure to 20 μM and 40 μM tadalafil were similar (P = 0.065, 0.195, and 0.130, respectively, for median amplitude, frequency, and AUCC).
Conclusion: Tadalafil reduces KCl-induced contractions of isolated human ureteral tissue in vitro. No incremental relaxations in contractions occurred by increasing the dose of tadalafil from 20 μM to 40 μM.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Moe OW. Kidney stones: Pathophysiology and medical management. Lancet. 2006;367:333–44. - PubMed
-
- Coll DM, Varanelli MJ, Smith RC. Relationship of spontaneous passage of ureteral calculi to stone size and location as revealed by unenhanced helical CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:101–3. - PubMed
-
- Roberts WW, Cadeddu JA, Micali S, Kavoussi LR, Moore RG. Ureteral stricture formation after removal of impacted calculi. J Urol. 1998;159:723–6. - PubMed
-
- Pickard R, Starr K, MacLennan G, Lam T, Cameron S, Norrie J, et al. Medical expulsive therapy in adults with ureteral colic: A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;386:341–9. - PubMed
-
- Jayant K, Agrawal R, Agrawal S. Tamsulosin versus tamsulosin plus tadalafil as medical expulsive therapy for lower ureteric stones: A randomized controlled trial. Int J Urol. 2014;21:1012–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

