Effect of polysaccharides from a Korean ginseng berry on the immunosenescence of aged mice
- PMID: 30337804
- PMCID: PMC6187098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.04.014
Effect of polysaccharides from a Korean ginseng berry on the immunosenescence of aged mice
Abstract
Background: Korean ginseng has been widely evaluated to treat human diseases; however, most studies on Korean ginseng have focused on its root. In this study, polysaccharides [acidic-polysaccharide-linked glycopeptide (APGP) extracted with 90% ethanol and hot water] were prepared from Korean ginseng berries, and their effect on immunosenescence was explored.
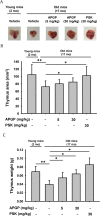
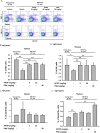
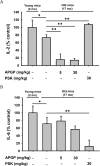
Methods: The effect of APGP on thymic involution was evaluated by measuring the size of thymi dissected from aged mice. The effect of APGP on populations of immune cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, dendritic cells, age-correlated CD11c-positive B cells, and several subtypes of T cells [CD4-positive, CD8-positive, and regulatory (Treg) T cells] in the thymi and spleens of aged mice was analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-6 were evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis. Profiles of APGP components were evaluated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis.
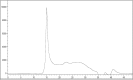
Results: APGP suppressed thymic involution by increasing the weight and areas of thymi in aged mice. APGP increased the population of NK cells, but showed no effect on the population of dendritic cells in the thymi and spleens of aged mice. APGP decreased the population of age-correlated CD11c-positive B cells in the spleens of aged mice. APGP showed no effect on the populations of CD4- and CD8-positive T cells in the thymi of aged mice, whereas it increased the population of Treg cells in the spleens of aged mice. APGP further decreased the reduced serum levels of IL-2 in aged mice, but serum levels of IL-6 were not statistically changed by APGP in aged mice. Finally, HPLC analysis showed that APGP had one major peak at 15 min (a main type of polysaccharide) and a long tail up to 35 min (a mixture of a variety of types of polysaccharides).
Conclusion: These results suggested that APGP exerted an anti-immunosenescent effect by suppressing thymic involution and modulating several types of immune cells.
Keywords: APGP; NK cell; Treg cell; ginseng berry; immunosenescence.
Figures



References
-
- Lipsky M.S., King M. Biological theories of aging. Dis Mon. 2015;61:460–466. - PubMed
-
- Robert L., Fulop T. Aging. Facts and theories. Preface. Interdiscip Top Gerontol. 2014;39:VI–VIII. - PubMed
-
- Solana R., Tarazona R., Gayoso I., Lesur O., Dupuis G., Fulop T. Innate immunosenescence: effect of aging on cells and receptors of the innate immune system in humans. Semin Immunol. 2012;24:331–341. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

