Gynura divaricata rich in 3, 5-/4, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and chlorogenic acid reduces islet cell apoptosis and improves pancreatic function in type 2 diabetic mice
- PMID: 30337946
- PMCID: PMC6180593
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-018-0310-y
Gynura divaricata rich in 3, 5-/4, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and chlorogenic acid reduces islet cell apoptosis and improves pancreatic function in type 2 diabetic mice
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic diseases that accompanied by severe complications. Gynura divaricata (GD), a medicinal and edible plant that is usually used for the treatment of diabetes. Therefore, this study investigates the chemical components of GD with hypoglycemic effect and the possible mechanism lowering blood sugar in T2D diabetic mice.
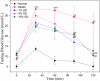
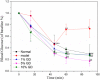
Methods: The methanol extract of GD was analysed by HPLC-DAD. And then mice with type 2 diabetes induced by a high-fat diet in combination with streptozotocin feed the diet containing lyophilized GD powder for 4 weeks. During this period, fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels and body weight were measured.
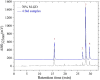
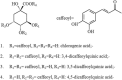
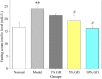
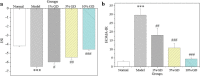
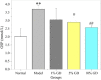
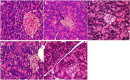
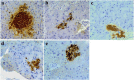
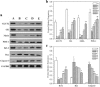
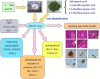
Results: GD was rich in four bioactive components of dicaffeoylquinic acid and chlorogenic acid. These components occupied about 2.37% in the GD powder in which the highest level was 3, 5-dicaffeoylquinic acid. Oral GD significantly reduced FBG, fasting serum insulin, and glycosylated serum protein levels, and enhanced antioxidative activities. HE-staining showed that the pathological damage in pancreatic β-cells was ameliorated. An immunohistochemical assay also showed that GD promoted marked pancreatic β-cell regeneration. GD also caused notable increase in GLUT2, GK, MafA, PDX-1, and Bcl-2 as well as reduction in Bax and caspase-3 expression as shown by western blot analysis.
Conclusions: GD exerts the pronounced hypoglycaemic effect by inhibiting islet cell apoptosis and improving pancreatic function. Therefore, GD might have a potential to improve diabetes.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Fasting blood glucose; Gynura divaricata; Pancreatic β-cell; Serum insulin; Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
All animal experimental protocols used in this study were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee at Soochow University (201504A136).No applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

