IRS-2 deubiquitination by USP9X maintains anchorage-independent cell growth via Erk1/2 activation in prostate carcinoma cell line
- PMID: 30338032
- PMCID: PMC6188063
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26049
IRS-2 deubiquitination by USP9X maintains anchorage-independent cell growth via Erk1/2 activation in prostate carcinoma cell line
Abstract
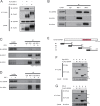
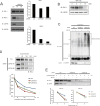
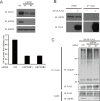
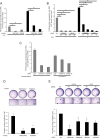
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) have been shown to induce proliferation of many types of cells. Insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) are major targets of IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) tyrosine kinase activated by IGFs, and are known to play important roles in the activation of downstream signaling pathways, such as the Erk1/2 pathway. Dysregulation of IGF signaling represents a central tumor promoting principle in human carcinogenesis. Prostate carcinoma is highly dependent on the IGF/IGF-IR/IRS axis. Here we identified the deubiquitinase, ubiquitin specific peptidase 9X (USP9X) as a novel binding partner of IRS-2. In a human prostate carcinoma cell line, small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of USP9X reduced IGF-IR as well as IRS-2 protein levels and increased their ubiquitination. Knockdown of USP9X suppressed basal activation of the Erk1/2 pathway, which was significantly restored by exogenous expression of IRS-2 but not by IGF-IR, suggesting that the stabilization of IRS-2 by USP9X is critical for basal Erk1/2 activation. Finally, we measured anchorage-independent cell growth, a characteristic cancer feature, by soft-agar colony formation assay. Knockdown of USP9X significantly reduced anchorage-independent cell growth of prostate carcinoma cell line. Taken all together, our findings indicate that USP9X is required for the promotion of prostate cancer growth by maintaining the activation of the Erk1/2 pathway through IRS-2 stabilization.
Keywords: IGF-I; IRS-2; USP9X; prostate cancer; ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Heidegger I, Kern J, Ofer P, Klocker H, Massoner P. Oncogenic functions of IGF1R and INSR in prostate cancer include enhanced tumor growth, cell migration and angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2014;5:2723–35. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1884 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heidegger I, Ofer P, Doppler W, Rotter V, Klocker H, Massoner P. Diverse functions of IGF / insulin signaling in malignant and noncancerous prostate cells : proliferation in cancer cells and differentiation in noncancerous cells. Endocrinology. 2012;153:4633–43. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1348. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dearth RK, Cui X, Kim HJ, Kuiatse I, Lawrence NA, Zhang X, Divisova J, Britton OL, Mohsin S, Allred DC, Hadsell DL, Lee AV. Mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis caused by overexpression of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) or IRS-2. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:9302–14. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00260-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

