Factors associated with self-management among Vietnamese adults with type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 30338096
- PMCID: PMC6178353
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.158
Factors associated with self-management among Vietnamese adults with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
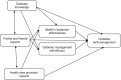
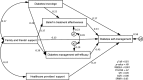
Aim: The study described diabetes self-management (DSM), diabetes knowledge, family and friends' support, healthcare providers' support, belief in treatment effectiveness and diabetes management self-efficacy, and explored DSM's associations among Vietnamese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Design: A cross-sectional design was applied.
Methods: The study used self-report questionnaires to collect data from 198 participants. Descriptive statistics and structural equation modelling (SEM) was used for data analysis.
Results: Vietnamese adults with T2DM performed DSM limitedly in certain aspects. They had strong belief in treatment effectiveness, good family and friends support, limited diabetes knowledge, healthcare professional support and self-efficacy. Their DSM was directly associated with diabetes knowledge, family and friends' support, healthcare providers' support, belief in treatment effectiveness and diabetes management self-efficacy. Their DSM was indirectly associated with diabetes knowledge and family and friends' support through their belief in treatment effectiveness and diabetes management self-efficacy.
Keywords: self‐efficacy; self‐management; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Asmamaw, A. , Asres, G. , Negese, D. , Fekadu, A. , & Assefa, G. (2015). Knowledge and attitude about diabetes mellitus and its associated factors among people in Debre Tabor town, Northwest Ethiopia: Cross sectional study. Science, 3, 199–209.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources