Body mass index and health-related quality of life
- PMID: 30338112
- PMCID: PMC6180707
- DOI: 10.1002/osp4.292
Body mass index and health-related quality of life
Abstract
Objective: There are conflicting data regarding the association between body mass index (BMI) and health-related quality of life (HRQoL), especially among certain population subgroups and for mental and physical health domains.
Methods: This study analysed the relationship between BMI and HRQoL (Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System mental and physical health scales) using ordinary least squares regression. Each model allowed for the possibility of a non-linear relationship between BMI and the outcome, adjusting for age, gender, comorbidities, diet and physical activity.
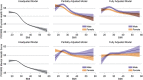
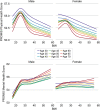
Results: A total of 10,133 respondents were predominantly female (71.7%), White (84.1%), median age of 52.1 years (interquartile range 37.2-63.3) and median BMI of 27.9 (interquartile range 24.0-33.2). In adjusted models, BMI was significantly associated with physical and mental HRQoL (p < 0.001). For physical HRQoL, there was a significant interaction with age (p = 0.02). For mental HRQoL, there was a significant interaction with sex (p = 0.0004) but not age (p = 0.7).
Conclusions: This study demonstrates a non-linear association of variable clinical relevance between BMI and HRQoL after adjusting for demographic factors and comorbidities. The relationship between BMI and HRQoL is nuanced and impacted by gender and age. These findings challenge the idea of obesity as a main driver of reduced HRQoL, particularly among women and with respect to mental HRQoL.
Keywords: Body mass index (BMI); epidemiology; public health; quality of life.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship of excess body weight and health-related quality of life: evidence from a population study in Taiwan.Int J Obes (Lond). 2006 Aug;30(8):1250-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803250. Epub 2006 Mar 7. Int J Obes (Lond). 2006. PMID: 16520814
-
Body mass index and health-related quality of life among young Swiss men.BMC Public Health. 2013 Oct 30;13:1028. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-1028. BMC Public Health. 2013. PMID: 24172041 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the relationship between body mass index and health-related quality of life in middle-aged or older Chinese adults].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Jul;30(7):687-91. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19957591 Chinese.
-
Exploring the nonlinear relationship between body mass index and health-related quality of life among adults: a cross-sectional study in Shaanxi Province, China.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015 Sep 23;13:153. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0347-9. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015. PMID: 26395980 Free PMC article.
-
Gender, race, BMI, and social support in relation to the health-related quality of life of cancer survivors: a report from the American Cancer Society's Study of Cancer Survivors II (SCS-II).Qual Life Res. 2016 Feb;25(2):409-421. doi: 10.1007/s11136-015-1084-6. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Qual Life Res. 2016. PMID: 26289021
Cited by
-
Association of pain and clinical factors on disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study from Turkish League Against Rheumatism Network.Arch Rheumatol. 2022 Nov 11;38(1):9-21. doi: 10.46497/ArchRheumatol.2023.9243. eCollection 2023 Mar. Arch Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 37235112 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of physical activity and body mass index on sleep quality and depression among Turkish adults.BMC Public Health. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):2618. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23912-9. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40753207 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related Quality of Life Increases After First-time Acute Myocardial Infarction: a Population-based Study.Zdr Varst. 2021 Dec 27;61(1):24-31. doi: 10.2478/sjph-2022-0005. eCollection 2022 Mar. Zdr Varst. 2021. PMID: 35111263 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related Quality of Life and Determinants of the Mental Dimension Among Tunisian Nurses in Public Hospitals.Med Lav. 2023 Feb 14;114(1):e2023002. doi: 10.23749/mdl.v114i1.13029. Med Lav. 2023. PMID: 36790411 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index having a mediating role between diet quality & mental and physical health among women.BMC Psychol. 2025 Apr 3;13(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02663-7. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40181473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guyatt GH, Feeny DH, Patrick DL. Measuring health‐related quality of life. Annals of Internal Medicine 1993; 118: 622–629. - PubMed
-
- Milder IE, de Hollander EL, Picavet HS, Verschuren WM, de Groot LC, Bemelmans WJ. Changes in weight and health‐related quality of life. The Doetinchem cohort study. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2014; 68: 471–477. - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Wu MJ, Ma XQ, et al. Body mass index and health‐related quality of life in adults: a population based study in five cities of China. European Journal of Public Health 2012; 22: 497–502. - PubMed
-
- Hassan MK, Joshi AV, Madhavan SS, Amonkar MM. Obesity and health‐related quality of life: a cross‐sectional analysis of the US population. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 2003; 27: 1227–1232. - PubMed
-
- Fontaine KR, Barofsky I. Obesity and health‐related quality of life. Obesity Reviews 2001; 2: 173–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
