Comparison of edema and ecchymosis in rhinoplasty candidates after lateral nasal osteotomy using piezosurgery and external osteotomy
- PMID: 30338232
- PMCID: PMC6174698
- DOI: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_294_18
Comparison of edema and ecchymosis in rhinoplasty candidates after lateral nasal osteotomy using piezosurgery and external osteotomy
Abstract
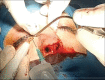
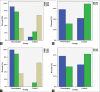
Rhinoplasty is done with external and endonasal methods. One of the main stages of rhinoplasty in both external and endonasal methods is the lateral nasal osteotomy. Lateral nasal osteotomy is the main cause of edema and ecchymosis after rhinoplasty, which is annoying and unpleasant for patients. Piezosurgery is a new method that uses electronic-ultrasonic waves to perform nasal osteotomies. The aim of this study was to compare of edema and ecchymosis after lateral nasal osteotomy using piezosurgery with external osteotomy in rhinoplasty candidates. In this clinical trial, 66 experimental patients for rhinoplasty surgery were selected from Imam Reza hospital in Tabriz, Iran. After examination, the patients were randomly divided into two groups. One group of patients had lateral nasal osteotomy by using the piezosurgery technique, and the other group had a lateral osteotomy with the conventional method of external subcutaneous. On the third and 7 days after the operation, the level of edema and ecchymosis in the patients were examined as per the Gökalan questionnaire (adopted by Yucel) by two persons who were not aware of the goals of the study, and then, they evaluated and scored the questionnaire. The obtained data were analyzed by the SPSS 19 software. The highest level of edema and ecchymosis was observed 3 days after surgery in both groups. Meanwhile, the findings revealed a significant difference between the two groups in the amount of edema and ecchymosis on day 3 after surgery. Furthermore on day 7, the amount of edema and ecchymosis compared to that of the 3rd day was statistically significant for both groups. In general, in all studied groups, edema, and ecchymosis decreased in 7 days compared to 3 days and also piezosurgery is more promising and effective than osteotomy.
Keywords: Ecchymosis; edema; lateral nasal osteotomy; piezosurgery; rhinoplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Robiony M, Toro C, Costa F, Sembronio S, Polini F, Politi M, et al. Piezosurgery: A new method for osteotomies in rhinoplasty. J Craniofac Surg. 2007;18:1098–100. - PubMed
-
- Vercellotti T. Piezoelectric surgery in implantology: A case report – A new piezoelectric ridge expansion technique. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2000;20:358–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
