Development and validation of a prognostic model for kidney function 1 year after combined pancreas and kidney transplantation using pre-transplant donor and recipient variables
- PMID: 30338375
- PMCID: PMC6244698
- DOI: 10.1007/s00423-018-1712-z
Development and validation of a prognostic model for kidney function 1 year after combined pancreas and kidney transplantation using pre-transplant donor and recipient variables
Abstract
Purpose: The widening gap between demand and supply of organs for transplantation provides extraordinary challenges for ethical donor organ allocation rules. The transplant community is forced to define favorable recipient/donor combinations for simultaneous kidney-pancreas transplantation. The aim of this study is the development of a prognostic model for the prediction of kidney function 1 year after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation using pre-transplant donor and recipient variables with subsequent internal and external validation.
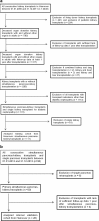
Methods: Included were patients with end-stage renal failure due to diabetic nephropathy. Multivariable logistic regression modeling was applied for prognostic model design with retrospective data from Hannover Medical School, Germany (01.01.2000-31.12.2011) followed by prospective internal validation (01 Jan. 2012-31 Dec. 2015). Retrospective data from another German transplant center in Kiel was retrieved for external model validation via the initially derived logit link function.
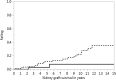
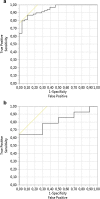
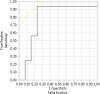
Results: The developed prognostic model is able to predict kidney graft function 1 year after transplantation ≥ KDIGO stage III with high areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve in the development cohort (0.943) as well as the internal (0.807) and external validation cohorts (0.784).
Conclusion: The proposed validated model is a valuable tool to optimize present allocation rules with the goal to prevent transplant futility. It might be used to support donor organ acceptance decisions for individual recipients.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy; Donor variables; Post-transplant graft function; Prognostic scores; Recipient variables; Simultaneous pancreas kidney transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Figures
Comment in
-
Invited commentary: advantages and cautions for developing valid prognostic models of simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation outcomes.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2022 Dec;407(8):3871-3873. doi: 10.1007/s00423-018-1729-3. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2022. PMID: 30421270 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolfe RA, Ashby VB, Milford EL, Ojo AO, Ettenger RE, Agodoa LY, Held PJ, Port FK. Comparison of mortality in all patients on dialysis, patients on dialysis awaiting transplantation, and recipients of a first cadaveric transplant. N Engl J Med. 1999;341(23):1725–1730. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199912023412303. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

