Incompatibility of the circadian protein BMAL1 and HNF4α in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30341289
- PMCID: PMC6195513
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06648-6
Incompatibility of the circadian protein BMAL1 and HNF4α in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
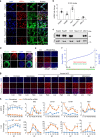
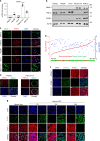
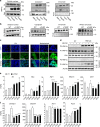
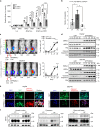
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α) is a master regulator of liver-specific gene expression with potent tumor suppressor activity, yet many liver tumors express HNF4α. This study reveals that P1-HNF4α, the predominant isoform expressed in the adult liver, inhibits expression of tumor promoting genes in a circadian manner. In contrast, an additional isoform of HNF4α, driven by an alternative promoter (P2-HNF4α), is induced in HNF4α-positive human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). P2-HNF4α represses the circadian clock gene ARNTL (BMAL1), which is robustly expressed in healthy hepatocytes, and causes nuclear to cytoplasmic re-localization of P1-HNF4α. We reveal mechanisms underlying the incompatibility of BMAL1 and P2-HNF4α in HCC, and demonstrate that forced expression of BMAL1 in HNF4α-positive HCC prevents the growth of tumors in vivo. These data suggest that manipulation of the circadian clock in HNF4α-positive HCC could be a tractable strategy to inhibit tumor growth and progression in the liver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have the following interests to report: F.M.S. is currently or has previously consulted for Ambys, Cell Design Labs (now part of Gilead Science). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hepatic circadian and differentiation factors control liver susceptibility for fatty liver disease and tumorigenesis.FASEB J. 2022 Sep;36(9):e22482. doi: 10.1096/fj.202101398R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 35947136 Free PMC article.
-
EPS15R, TASP1, and PRPF3 are novel disease candidate genes targeted by HNF4alpha splice variants in hepatocellular carcinomas.Gastroenterology. 2008 Apr;134(4):1191-202. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.01.027. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18395097
-
Protein arginine methyl transferase 1- and Jumonji C domain-containing protein 6-dependent arginine methylation regulate hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha expression and hepatocyte proliferation in mice.Hepatology. 2018 Mar;67(3):1109-1126. doi: 10.1002/hep.29587. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Hepatology. 2018. PMID: 29023917 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha in Liver Cancer.Semin Liver Dis. 2024 Aug;44(3):383-393. doi: 10.1055/a-2349-7236. Epub 2024 Jun 20. Semin Liver Dis. 2024. PMID: 38901435 Review.
-
Deregulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 (HNF4)as a marker of epithelial tumors progression.Exp Oncol. 2010 Sep;32(3):167-71. Exp Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21403612 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00858 exerts a tumor-promoting role in colon cancer via HNF4α and WNK2 regulation.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Apr;43(2):297-310. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00490-8. Epub 2019 Dec 28. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31884577
-
Nuclear p62/SQSTM1 facilitates ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation of BMAL1.PLoS Genet. 2025 Jul 10;21(7):e1011794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011794. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40638681 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between the PI3K/AKT pathway and circadian clock in physiologic and cancer-related pathologic conditions.Cell Prolif. 2024 Jul;57(7):e13608. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13608. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38336976 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of p-STAT3 and c-Myc correlates with P2-HNF4α expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Oncotarget. 2022 Dec 6;13:1308-1313. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28324. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 36473131 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian Oscillation of Natural Antisense Transcripts Related to Human Core Clock Genes.Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Oct;10(3):471-476. doi: 10.52547/rbmb.10.3.471. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34981025 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM114424/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK092590/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- DK114037/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- R01 DK109001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056338/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK109001/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- RSG-17-215-01-C/American Cancer Society (American Cancer Society, Inc.)/International
- DK09470/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- R01 CA230848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK114037/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK053895/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- R01 DK092590/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

