Mycobacterial DnaB helicase intein as oxidative stress sensor
- PMID: 30341292
- PMCID: PMC6195587
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06554-x
Mycobacterial DnaB helicase intein as oxidative stress sensor
Abstract
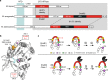
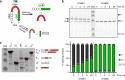
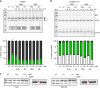
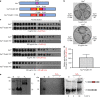
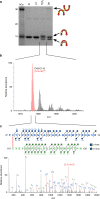
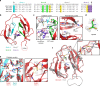
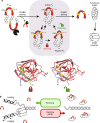
Inteins are widespread self-splicing protein elements emerging as potential post-translational environmental sensors. Here, we describe two inteins within one protein, the Mycobacterium smegmatis replicative helicase DnaB. These inteins, DnaBi1 and DnaBi2, have homology to inteins in pathogens, splice with vastly varied rates, and are differentially responsive to environmental stressors. Whereas DnaBi1 splicing is reversibly inhibited by oxidative and nitrosative insults, DnaBi2 is not. Using a reporter that measures splicing in a native intein-containing organism and western blotting, we show that H2O2 inhibits DnaBi1 splicing in M. smegmatis. Intriguingly, upon oxidation, the catalytic cysteine of DnaBi1 forms an intramolecular disulfide bond. We report a crystal structure of the class 3 DnaBi1 intein at 1.95 Å, supporting our findings and providing insight into this splicing mechanism. We propose that this cysteine toggle allows DnaBi1 to sense stress, pausing replication to maintain genome integrity, and then allowing splicing immediately when permissive conditions return.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conditional DnaB Protein Splicing Is Reversibly Inhibited by Zinc in Mycobacteria.mBio. 2020 Jul 14;11(4):e01403-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01403-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32665276 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Chlorine Species Reversibly Inhibit DnaB Protein Splicing in Mycobacteria.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0030121. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00301-21. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34549994 Free PMC article.
-
The Arthrobacter species FB24 Arth_1007 (DnaB) intein is a pseudogene.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026361. Epub 2011 Oct 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22028863 Free PMC article.
-
Inteins as targets for potential antimycobacterial drugs.Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1157-65. doi: 10.2741/1195. Front Biosci. 2003. PMID: 12957838 Review.
-
Inteins-mechanism of protein splicing, emerging regulatory roles, and applications in protein engineering.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 8;14:1305848. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1305848. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conditional DnaB Protein Splicing Is Reversibly Inhibited by Zinc in Mycobacteria.mBio. 2020 Jul 14;11(4):e01403-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01403-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32665276 Free PMC article.
-
SufB intein splicing in Mycobacterium tuberculosis is influenced by two remote conserved N-extein histidines.Biosci Rep. 2022 Mar 31;42(3):BSR20212207. doi: 10.1042/BSR20212207. Biosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35234249 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Single-Stranded DNA Activation of Recombinase Intein Splicing.Biochemistry. 2019 Aug 6;58(31):3335-3339. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00506. Epub 2019 Jul 23. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31318538 Free PMC article.
-
Thermally controlled intein splicing of engineered DNA polymerases provides a robust and generalizable solution for accurate and sensitive molecular diagnostics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jun 23;51(11):5883-5894. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad368. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37166959 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Quantitation of a Selectable Protein Splicing Sensor Using Gibson Assembly and Spot Titers.Curr Protoc. 2021 Mar;1(3):e82. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.82. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33739627 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P41GM103393/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)/International
- R37 GM039422/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32GM121000/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)/International
- DE-AC02-76SF00515/U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)/International
- F32 GM121000/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32AI055429/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)/International
- GM39422/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)/International
- R01 GM039422/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI055429/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM044844/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

