Alternative processing of its precursor is related to miR319 decreasing in melon plants exposed to cold
- PMID: 30341377
- PMCID: PMC6195573
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34012-7
Alternative processing of its precursor is related to miR319 decreasing in melon plants exposed to cold
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Alternative processing of its precursor is related to miR319 decreasing in melon plants exposed to cold.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 2;12(1):18512. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22793-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36323757 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
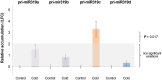
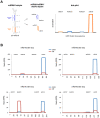
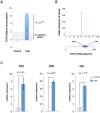
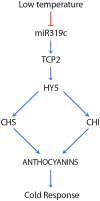
miRNAs are fundamental endogenous regulators of gene expression in higher organisms. miRNAs modulate multiple biological processes in plants. Consequently, miRNA accumulation is strictly controlled through miRNA precursor accumulation and processing. Members of the miRNA319 family are ancient ribo-regulators that are essential for plant development and stress responses and exhibit an unusual biogenesis that is characterized by multiple processing of their precursors. The significance of the high conservation of these non-canonical biogenesis pathways remains unknown. Here, we analyze data obtained by massive sRNA sequencing and 5' - RACE to explore the accumulation and infer the processing of members of the miR319 family in melon plants exposed to adverse environmental conditions. Sequence data showed that miR319c was down regulated in response to low temperature. However, the level of its precursor was increased by cold, indicating that miR319c accumulation is not related to the stem loop levels. Furthermore, we found that a decrease in miR319c was inversely correlated with the stable accumulation of an alternative miRNA (#miR319c) derived from multiple processing of the miR319c precursor. Interestingly, the alternative accumulation of miR319c and #miR319c was associated with an additional and non-canonical partial cleavage of the miR319c precursor during its loop-to-base-processing. Analysis of the transcriptional activity showed that miR319c negatively regulated the accumulation of HY5 via TCP2 in melon plants exposed to cold, supporting its involvement in the low temperature signaling pathway associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis. Our results provide new insights regarding the versatility of plant miRNA processing and the mechanisms regulating them as well as the hypothetical mechanism for the response to cold-induced stress in melon, which is based on the alternative regulation of miRNA biogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures