Golgi protein 73 and its diagnostic value in liver diseases
- PMID: 30341783
- PMCID: PMC6496820
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12538
Golgi protein 73 and its diagnostic value in liver diseases
Abstract
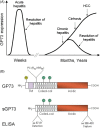
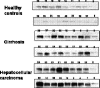
Golgi protein 73 (GP73, also referred to as Golph 2) with 400 amino acids is a 73 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein typically found in the cis-Golg complex. It is primarily expressed in epithelial cells, which has been found upregulated in hepatocytes in patients suffering from both viral and non-viral liver diseases. GP73 has drawn increasing attention for its potential application in the diagnosis of liver diseases such as hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Herein, we reviewed the discovery history of GP73 and summarized studies by many groups around the world, aiming at understanding its structure, expression, function, detection methods and the relationship between GP73 and liver diseases in various settings.
Keywords: GP73; hepatitis; liver cancer; liver cirrhosis.
© 2018 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Golgi protein-73: A biomarker for assessing cirrhosis and prognosis of liver disease patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Sep 14;26(34):5130-5145. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5130. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32982114 Free PMC article.
-
Possible roles of Golgi protein-73 in liver diseases.Ann Hepatol. 2022 Sep-Oct;27(5):100720. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2022.100720. Epub 2022 May 14. Ann Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35577277 Review.
-
Golgi protein 73(GP73), a useful serum marker in liver diseases.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011 Aug;49(8):1311-1316. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2011.640. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. PMID: 21663469
-
Whether the Golgi protein 73 could be a diagnostic serological marker in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Mar 24;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02685-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36964524 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of Golgi protein 73 in differentiating benign from malignant liver tumors.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 17;9(7):e100187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100187. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25033446 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Serum golgi protein-73 (GP-73) in children with autoimmune hepatitis.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 Sep 3;184(9):592. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06428-7. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40903626 Free PMC article.
-
Profibrotic Signaling and HCC Risk during Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Biomarker Development.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 2;10(5):977. doi: 10.3390/jcm10050977. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33801181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for discovering novel hepatocellular carcinoma biomarkers.World J Hepatol. 2025 Feb 27;17(2):101201. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.101201. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40027561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Superior Diagnostic Efficacy of N-Terminal Propeptide of Type III Collagen and Golgi Protein 73 for Detection of Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jun 11;6(6):e70236. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70236. eCollection 2025 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40502814 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances of GOLM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepat Oncol. 2020 Jun 29;7(2):HEP22. doi: 10.2217/hep-2020-0006. Hepat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32647567 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xia Y, Yao A, Xu H, et al. Comparison of two latex nanoparticles with different diameters and the application in detection of biomarker golgi protein 73 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nanosci Nanotech Lett. 2017;9:398‐405.
-
- Xu WF, Fei YM, Zhou JK, et al. Significance of serum golgi protein 73 (GP73), alpha‐fetoprotein (AFP) and lectin‐reactive alpha‐fetoprotein (AFP‐L3) expression in primary hepatic carcinoma. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2011;25:286‐288. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Liu Q, Zhang H, et al. Silencing of GP73 inhibits invasion and metastasis via suppression of epithelial‐mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2017;37:1182‐1188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BJ16003/Health Care for Cadres Research Fund of Jiangsu Province
- ZDRCA2016065/Jiangsu Province Medical Talent
- 61527806/National Natural Scientific Foundation of China
- 61741114/National Natural Scientific Foundation of China
- 81472831/National Natural Scientific Foundation of China
- 81700790/National Natural Scientific Foundation of China
- 201705/Opening Project of State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics
- BE2016625/Key Research and Development Project of Jiangsu Province
- 201715020/Science and Technology Development Program of Nanjing
- ZKX16045/Medical Key Science and Technology Development Projects of Nanjing
- SKLOD2018OF02/Open Funding of State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

