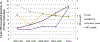Increasing prevalence of high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma on index endoscopy in Barrett's esophagus over the past 2 decades: data from a multicenter U.S. consortium
- PMID: 30342028
- PMCID: PMC7053563
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.09.041
Increasing prevalence of high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma on index endoscopy in Barrett's esophagus over the past 2 decades: data from a multicenter U.S. consortium
Abstract
Introduction: Data on time trends of dysplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) in Barrett's esophagus (BE) during the index endoscopy (ie, prevalent cases) are limited. Our aim was to determine the prevalence patterns of BE-associated dysplasia on index endoscopy over the past 25 years.
Methods: The Barrett's Esophagus Study is a multicenter outcome project of a large cohort of patients with BE. Proportions of patients with index endoscopy findings of no dysplasia (NDBE), low-grade dysplasia (LGD), high-grade dysplasia (HGD), and EAC were extracted per year of index endoscopy, and 5-yearly patient cohorts were tabulated over years 1990 to 2010+ (2010-current). Prevalent dysplasia and endoscopic findings were trended over the past 25 years using percentage dysplasia (LGD, HGD, EAC, and HGD/EAC) to assess changes in detection of BE-associated dysplasia over the last 25 years. Statistical analysis was done using SAS version 9.4 software (SAS, Cary, NC).
Results: A total of 3643 patients were included in the analysis with index endoscopy showing NDBE in 2513 (70.1%), LGD in 412 (11.5%), HGD in 193 (5.4%), and EAC in 181 (5.1%). Over time, there was an increase in the mean age of patients with BE (51.7 ± 29 years vs 62.6 ± 11.3 years) and the proportion of males (84% vs 92.6%) diagnosed with BE but a decrease in the mean BE length (4.4±4.3 cm vs 2.9±3.0 cm) as time progressed (1990-1994 to 2010-2016 time periods). The presence of LGD on index endoscopy remained stable over 1990 to 2016. However, a significant increase (148% in HGD and 112% in EAC) in the diagnosis of HGD, EAC, and HGD/EAC was noted on index endoscopy over the last 25 years (P < .001). There was also a significant increase in the detection of visible lesions on index endoscopy (1990-1994, 5.1%; to 2005-2009, 6.3%; and 2010+, 16.3%) during the same period.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the prevalence of HGD and EAC has significantly increased over the past 25 years despite a decrease in BE length during the same period. This increase parallels an increase in the detection of visible lesions, suggesting that a careful examination at the index examination is crucial.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Pohl H, Welch HG. The role of overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97:142–6. - PubMed
-
- Schneider JL, Corley DA. The troublesome epidemiology of Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2017;27:353–64. - PubMed
-
- Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK. The changing epidemiology of esophageal cancer. Semin Oncol 1999;26(5 Suppl 15):2–8. - PubMed
-
- Botterweck AA, Schouten LJ, Volovics A, et al. Trends in incidence of adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus and gastric cardia in ten European countries. Int J Epidemiol 2000;29:645–54. - PubMed
-
- Vizcaino AP, Moreno V, Lambert R, et al. Time trends incidence of both major histologic types of esophageal carcinomas in selected countries, 1973–1995. Int J Cancer 2002;99:860–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous