Therapeutic potential of targeting the Eph/ephrin signaling complex
- PMID: 30343150
- PMCID: PMC6457248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.10.006
Therapeutic potential of targeting the Eph/ephrin signaling complex
Abstract
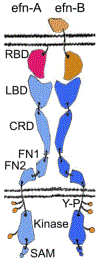
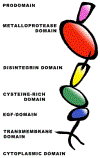
The Eph-ephrin signaling pathway mediates developmental processes and the proper functioning of the adult human body. This distinctive bidirectional signaling pathway includes a canonical downstream signal cascade inside the Eph-bearing cells, as well as a reverse signaling in the ephrin-bearing cells. The signaling is terminated by ADAM metalloproteinase cleavage, internalization, and degradation of the Eph/ephrin complexes. Consequently, the Eph-ephrin-ADAM signaling cascade has emerged as a key target with immense therapeutic potential particularly in the context of cancer. An interesting twist was brought forth by the emergence of ephrins as the entry receptors for the pathological Henipaviruses, which has spurred new studies to target the viral entry. The availability of high-resolution structures of the multi-modular Eph receptors in complexes with ephrins and other binding partners, such as peptides, small molecule inhibitors and antibodies, offers a wealth of information for the structure-guided development of therapeutic intervention. Furthermore, genomic data mining of Eph mutants involved in cancer provides information for targeted drug development. In this review we summarize the distinct avenues for targeting the Eph-ephrin signaling pathway, including its termination by ADAM proteinases. We highlight the latest developments in Eph-related pharmacology in the context of Eph-ephrin-ADAM-based antibodies and small molecules. Finally, the future prospects of genomics- and proteomics-based medicine are discussed.
Keywords: ADAM proteinase; Antibody drug; Eph receptor; Eph-specific peptide; Small molecule inhibitor.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Abengozar MA, de Frutos S, Ferreiro S, Soriano J, Perez-Martinez M, Olmeda D, Marenchino M, Canamero M, Ortega S, Megias D, Rodriguez A and Martinez-Torrecuadrada JL (2012) Blocking ephrinB2 with highly specific antibodies inhibits angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and tumor growth. Blood 119:4565–4576. - PubMed
-
- Amero P, Esposito CL, Rienzo A, Moscato F, Catuogno S and de Franciscis V (2016) Identification of an Interfering Ligand Aptamer for EphB2/3 Receptors. Nucleic Acid Ther 26:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous (2013) Nipah encephalitis, human - Bangladesh (05), in Pro-med, International Society for Infectious Diseases.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

