Longer Follow-Up Confirms Relapse-Free Survival Benefit With Adjuvant Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With Resected BRAF V600-Mutant Stage III Melanoma
- PMID: 30343620
- PMCID: PMC6286159
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.18.01219
Longer Follow-Up Confirms Relapse-Free Survival Benefit With Adjuvant Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With Resected BRAF V600-Mutant Stage III Melanoma
Abstract
Purpose: Dabrafenib plus trametinib improved relapse-free survival (RFS) versus placebo (hazard ratio [HR], 0.47; P < .001) in patients with resected BRAF V600-mutant stage III melanoma (BRF115532; COMBI-AD; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01682083). We present an updated RFS analysis on the basis of extended study follow-up and a cure-rate model analysis to estimate the fraction of patients expected to remain relapse free long term.
Methods: In this phase III trial, patients with resected BRAF V600-mutant stage III melanoma were randomly assigned to 12 months of adjuvant dabrafenib plus trametinib versus placebo. We report updated RFS (primary end point) and distant metastasis-free survival. RFS was also analyzed by subgroups defined by baseline disease stage (American Joint Committee on Cancer 7th and 8th editions), nodal metastatic burden, and ulceration status. The fraction of patients who remained relapse free long term was estimated using a Weibull mixture cure-rate model.
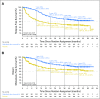
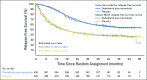
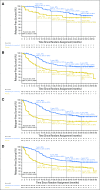
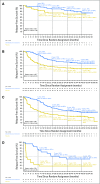
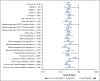
Results: At median follow-up of 44 months (dabrafenib plus trametinib) and 42 months (placebo), 3- and 4-year RFS rates were 59% (95% CI, 55% to 64%) and 54% (95% CI, 49% to 59%) in the dabrafenib plus trametinib arm and 40% (95% CI, 35% to 45%) and 38% (95% CI, 34% to 44%) in the placebo arm, respectively (HR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.40 to 0.59). Distant metastasis-free survival also favored dabrafenib plus trametinib (HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.67). The estimated cure rate was 54% (95% CI, 49% to 59%) in the dabrafenib plus trametinib arm compared with 37% (95% CI, 32% to 42%) in the placebo arm. Subgroup analysis of RFS demonstrated similar treatment benefit regardless of baseline factors, including disease stage, nodal metastatic burden, and ulceration.
Conclusion: Longer follow-up confirmed RFS benefit with dabrafenib plus trametinib. Subgroup analysis suggested that dabrafenib plus trametinib benefited patients regardless of baseline factors.
Figures
Comment in
-
Reply to E. Hindié and K.R. Hess.J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 20;37(15):1356-1358. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00004. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30939092 No abstract available.
-
What Is the Role of Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib Adjuvant Therapy in Stage IIIA Melanoma?J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 20;37(15):1355-1356. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.02075. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30939094 No abstract available.
-
Beneficial Effect of Adjuvant Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib on Recurrence-Free Survival in Patients With Resected BRAFV600-Mutant Stage III Melanoma Seems to be Short-Lived.J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 20;37(15):1354-1355. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01768. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30939097 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ugurel S, Röhmel J, Ascierto PA, et al. : Survival of patients with advanced metastatic melanoma: The impact of novel therapies-update 2017. Eur J Cancer 83:247-257, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, et al. : Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in resected stage III or IV melanoma. N Engl J Med 377:1824-1835, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Weber JS, Mandalà M, Del Vecchio M, et al. : Adjuvant therapy with nivolumab (NIVO) versus ipilimumab (IPI) after complete resection of stage III/IV melanoma: Updated results from a phase III trial (CheckMate 238). J Clin Oncol 36:18s, 2018. (suppl; abstr 9502)
-
- Eggermont AMM, Blank CU, Mandala M, et al. : Adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in resected stage III melanoma. N Engl J Med 378:1789-1801, 2018 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

