Persistent cervical lymphadenitis in a patient with prior thyroid cancer attributed to Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease
- PMID: 30344150
- PMCID: PMC6202984
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-226457
Persistent cervical lymphadenitis in a patient with prior thyroid cancer attributed to Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease
Abstract
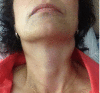
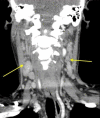
We describe a 50-year-old woman with a history of thyroid cancer who presented with bilateral cervical and submandibular lymphadenopathy, low-grade fevers, and increasing fatigue. The patient underwent lymph node fine-needle aspiration, which showed no evidence of metastatic or lymphoproliferative disease. This procedure was complicated by a parapharyngeal abscess and cellulitis. She was treated unsuccessfully with various courses of antibiotics, but briefly responded to short courses of steroids. As her cervical lymphadenopathy returned, she underwent an excisional lymph node biopsy, which demonstrated caseating granulomatous lymphadenitis. Extensive review of systems, physical examination, laboratory and imaging studies demonstrated no evidence of malignancy, infection or systemic lupus erythematosus . Our patient was clinically diagnosed with Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease and successfully treated with prednisone tapered over 3 months. She remains in clinical remission.
Keywords: connective tissue disease; malignant and benign haematology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2018. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kikuchi M. Lymphadenitis showing focal reticulum cell hyperplasia with nuclear debris and phagocytosis. Nippon Ketsueki Gakkai Zasshi 1972;35:378–80.
-
- Fujimoto Y, Kozima Y, Hamaguchi K. Cervical necrotizing lymphadenitis: a new clinicopathological agent. Naika 1972;20:920–7.
-
- Dorfman RF. Histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis of Kikuchi and Fujimoto. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1987;111:1026–9. - PubMed
-
- Dorfman RF, Berry GJ. Kikuchi’s histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis: an analysis of 108 cases with emphasis on differential diagnosis. Semin Diagn Pathol 1988;5:329–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials