Correction of hypovitaminosis D improved global longitudinal strain earlier than left ventricular ejection fraction in cardiovascular older adults after orthopaedic surgery
- PMID: 30344531
- PMCID: PMC6188939
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2018.08.005
Correction of hypovitaminosis D improved global longitudinal strain earlier than left ventricular ejection fraction in cardiovascular older adults after orthopaedic surgery
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular diseases and insufficient levels of vitamin D are risk factors for adverse surgical outcomes, and they are both commonly present among older adults undergoing orthopaedic surgery. Giving the cardiovascular effects of vitamin D, pre-operative diagnosis of hypovitaminosis D would be a valuable step for the implementation of supplementation protocols. We investigated if the normalization of serum 25 [OH] D could ameliorate cardiac performance of older adults suffering from cardiovascular diseases.
Methods: We enrolled 47 older adults scheduled for major orthopaedic surgery and suffering from hypovitaminosis D. Patients underwent 6-months calcifediol supplementation with a starting dose at first post-operative day of 50 µg/die in liquid preparation. Down-titration to 20 µg/die at 3-months assessment was planned. Cardiac performance was evaluated by measuring left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and global longitudinal strain (GLS) during pre-operative assessments and at 1-month, 3-months, 6-months follow-ups.
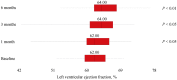
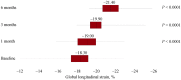
Results: Six months of calcifediol supplementation were associated with a significant improvement of both LVEF (+ 3.94%; 95% CI: -4.0789 to -0.8232; P < 0.01) and GLS (+ 18.56%; Z = -5.895; P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Calcifediol supplementation normalized serum 25 [OH] D concentration after 1-month treatment. GLS offered better insights into myocardial contractile amelioration than LVEF, thus being useful for detecting earlier subclinical changes that may anticipate hemodynamic modifications.
Keywords: Global longitudinal strain; Left ventricular ejection fraction; Orthopedic surgery; Transthoracic echocardiography; Vitamin D.
Figures

References
-
- Sprague S, Petrisor B, Scott T, et al. What is the role of vitamin D supplementation in acute fracture patients? A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of hypovitaminosis D and Supplementation efficacy. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Sathiyakumar V, Avilucea FR, Whiting PS, et al. Risk factors for adverse cardiac events in hip fracture patients: an analysis of NSQIP data. Int Orthop. 2016;40:439–445. - PubMed
-
- Matsen FA, 3rd, Li N, Gao H, et al. Factors affecting length of stay, readmission, and revision after shoulder arthroplasty: a population-based study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97:1255–1263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
