Toxic effects of four kinds of dental restorative materials on fibroblast HGF-1 and impacts on expression of Bcl-2 and Bax genes
- PMID: 30344691
- PMCID: PMC6176157
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6705
Toxic effects of four kinds of dental restorative materials on fibroblast HGF-1 and impacts on expression of Bcl-2 and Bax genes
Abstract
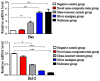
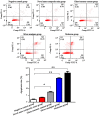
The aim of this study was to investigate and discuss the toxic effect of four kinds of dental restorative materials on fibroblast HGF-1 and their impacts on the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) and Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) genes. One hundred and ninety-two patients (240 diseased teeth), who received dental restoration in the Department of Stomatology of Xuzhou Stomatology Hospital from March 2014 to March 2015, were selected and randomly divided into four groups; namely, silver amalgam group, glass-ionomer cement group, nichrome group and novel nano-composite resin group, with 60 teeth in each group. The diseased teeth were restored. The fibroblast HGF-1 was incubated in the water extracts from the four kinds of materials and ordinary cell culture fluid (negative control). Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and western blotting were used to measure the levels of Bcl-2 and Bax. A flow cytometer was applied to detect cell apoptosis. RT-qPCR results showed that compared with those in the negative control group, the mRNA expression levels of Bcl-2 in the cells of silver amalgam group, glass-ionomer cement group and nichrome group were decreased, while those of Bax were upregulated (P<0.05). The mRNA expression of Bcl-2 in glass-ionomer cement group was the highest among these three groups; the mRNA expression of Bax in nichrome group was the highest of all groups. The western blotting results revealed the same tendency as those of RT-qPCR. The results via the flow cytometer showed that cell apoptosis in nichrome group, silver amalgam group and glass-ionomer cement group was increased significantly (P<0.05) compared with that in the negative control group. The novel nano-composite resin has no obvious toxic effect on cells, and its clinical application effect is better than that of traditional dental restorative materials, which is worthy of application and generalization in clinical practice.
Keywords: apoptosis; cytotoxicity; dental restoration; glass-ionomer cement; nano-composite resin; nichrome; silver amalgam.
Figures

References
-
- Kawajiri H, Yamanami M, Mizuno T, Kanda K, Yaku H, Nakayama Y. Feasibility of connective tissue membrane (bio-sheet) prepared in the body as cardiovascular repair material as a substitute for self-pericardium. Circulation. 2013;128:A12910.
-
- Croll TP, Berg JH, Donly KJ. Dental repair material: A resin-modified glass-ionomer bioactive ionic resin-based composite. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2015;36:60–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
