Prominent role of histone lysine demethylases in cancer epigenetics and therapy
- PMID: 30344952
- PMCID: PMC6188137
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24319
Prominent role of histone lysine demethylases in cancer epigenetics and therapy
Abstract
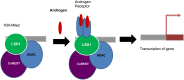
Protein methylation has an important role in the regulation of chromatin, gene expression and regulation. The protein methyl transferases are genetically altered in various human cancers. The enzymes that remove histone methylation have led to increased awareness of protein interactions as potential drug targets. Specifically, Lysine Specific Demethylases (LSD) removes methylated histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) and H3 lysine 9 (H3K9) through formaldehyde-generating oxidation. It has been reported that LSD1 and its downstream targets are involved in tumor-cell growth and metastasis. Functional studies of LSD1 indicate that it regulates activation and inhibition of gene transcription in the nucleus. Here we made a discussion about the summary of histone lysine demethylase and their functions in various human cancers.
Keywords: epigenetics; histone modifications; lysine specific demethylases; protein methylation; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There is no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

