Function of Serine Protease HtrA in the Lifecycle of the Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni
- PMID: 30345086
- PMCID: PMC6186014
- DOI: 10.1556/1886.2018.00011
Function of Serine Protease HtrA in the Lifecycle of the Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni
Abstract
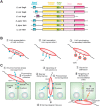
Campylobacter jejuni is a major food-borne zoonotic pathogen, responsible for a large proportion of bacterial gastroenteritis cases, as well as Guillian-Barré and Miller-Fisher syndromes. During infection, tissue damage is mainly caused by bacteria invading epithelial cells and traversing the intestinal barrier. C. jejuni is able to enter the lamina propria and the bloodstream and may move into other organs, such as spleen, liver, or mesenteric lymph nodes. However, the involved molecular mechanisms are not fully understood. C. jejuni can transmigrate effectively across polarized intestinal epithelial cells mainly by the paracellular route using the serine protease high-temperature requirement A (HtrA). However, it appears that HtrA has a dual function, as it also acts as a chaperone, interacting with denatured or misfolded periplasmic proteins under stress conditions. Here, we review recent progress on the role of HtrA in C. jejuni pathogenesis. HtrA can be transported into the extracellular space and cleaves cell-to-cell junction factors, such as E-cadherin and probably others, disrupting the epithelial barrier and enabling paracellular transmigration of the bacteria. The secretion of HtrA is a newly discovered strategy also utilized by other pathogens. Thus, secreted HtrA proteases represent highly attractive targets for anti-bacterial treatment and may provide a suitable candidate for vaccine development.
Keywords: C. jejuni proteases; E-cadherin; HtrA; LOS; TER; adherens junction; cellular invasion; fibronectin; integrins; molecular pathogenesis; occludin; outer membrane vesicles (OMVs); signaling; tight junction; virulence.
Figures
References
-
- Nachamkin I, Szymanski CM, Blaser MJ. Campylobacter. Washington (DC): ASM Press; 2008.
-
- Dasti JI, Tareena AM, Lugerta R, Zautnera AE, Groß U. Campylobacter jejuni: a brief overview on pathogenicity- associated factors and disease-mediating mechanisms. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010;300:205–11. - PubMed
-
- Forsythe SJ. Food poisoning microorganisms. In: The Microbiology of Safe Food. Forsythe SJ, editor. Abingdon: Blackwell Science Publishers; 2000:87–148.
-
- World Health Organization. Global burden of disease (GBD) 2002 estimates. WHO 2008; Geneva, Switzerland: Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/global_burden_of_disease/en/.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
