Therapeutic applications of genetic code expansion
- PMID: 30345400
- PMCID: PMC6190509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.synbio.2018.09.003
Therapeutic applications of genetic code expansion
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020 Oct 14;5(4):330-331. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2020.10.001. eCollection 2020 Dec. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33102827 Free PMC article.
Abstract
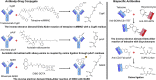
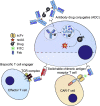
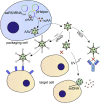
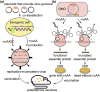
In nature, a limited, conservative set of amino acids are utilized to synthesize proteins. Genetic code expansion technique reassigns codons and incorporates noncanonical amino acids (ncAAs) through orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS)/tRNA pairs. The past decade has witnessed the rapid growth in diversity and scope for therapeutic applications of this technology. Here, we provided an update on the recent progress using genetic code expansion in the following areas: antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), bispecific antibodies (BsAb), immunotherapies, long-lasting protein therapeutics, biosynthesized peptides, engineered viruses and cells, as well as other therapeutic related applications, where the technique was used to elucidate the mechanisms of biotherapeutics and drug targets.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugates; Biotherapeutics; Genetic code expansion; Live-attenuated vaccines; Noncanonical amino acids.
Figures

References
-
- Wang L., Magliery T.J., Liu D.R., Schultz P.G. A new functional suppressor tRNA/aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pair for the in vivo incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:5010–5011.
-
- Wang L., Brock A., Herberich B., Schultz P.G. Expanding the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Science. 2001;292:498–500. - PubMed
-
- Neumann H., Wang K., Davis L., Garcia-Alai M., Chin J.W. Encoding multiple unnatural amino acids via evolution of a quadruplet-decoding ribosome. Nature. 2010;464:441–444. - PubMed
-
- Blight S.K., Larue R.C., Mahapatra A., Longstaff D.G., Chang E., Zhao G. Direct charging of tRNA(CUA) with pyrrolysine in vitro and in vivo. Nature. 2004;431:333–335. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

