The synthetic cathinones, butylone and pentylone, are stimulants that act as dopamine transporter blockers but 5-HT transporter substrates
- PMID: 30345459
- PMCID: PMC6476708
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5075-5
The synthetic cathinones, butylone and pentylone, are stimulants that act as dopamine transporter blockers but 5-HT transporter substrates
Abstract
Rationale: Synthetic cathinones continue to emerge in recreational drug markets worldwide. 1-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)butan-1-one (butylone) and 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)pentan-1-one (pentylone) are derivatives of the cathinone compound, 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-2-(methylamino)propan-1-one (methylone), that are being detected in drug products and human casework.
Objectives: The purpose of the present study was to examine the neuropharmacology of butylone and pentylone using in vitro and in vivo methods.
Methods: In vitro uptake and release assays were carried out in rat brain synaptosomes and in cells expressing human dopamine transporters (DAT) and 5-HT transporters (SERT). In vivo microdialysis was performed in the nucleus accumbens of conscious rats to assess drug-induced changes in neurochemistry.
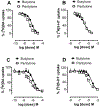
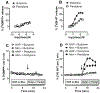
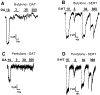
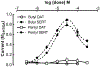
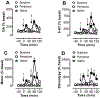
Results: Butylone and pentylone were efficacious uptake blockers at DAT and SERT, though pentylone was more DAT-selective. Both drugs acted as transporter substrates that evoked release of [3H]5-HT at SERT, while neither evoked release at DAT. Consistent with the release data, butylone and pentylone induced substrate-associated inward currents at SERT but not DAT. Administration of butylone or pentylone to rats (1 and 3 mg/kg, i.v.) increased extracellular monoamines and motor activity, but pentylone had weaker effects on 5-HT and stronger effects on motor stimulation.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that increasing the α-carbon chain length of methylone creates "hybrid" transporter compounds which act as DAT blockers but SERT substrates. Nevertheless, butylone and pentylone elevate extracellular dopamine and stimulate motor activity, suggesting both drugs possess significant risk for abuse.
Keywords: 5-HT; Cathinone; Dopamine; Microdialysis; Neurochemistry; Transporter.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
H.H.S. has received honoraria for lectures and consulting from Lundbeck, Ratiopharm, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Serumwerk Bernburg. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
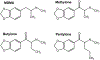
References
-
- Baumann MH, Bulling S, Benaderet TS, Saha K, Ayestas MA, Partilla JS, Ali SF, Stockner T, Rothman RB, Sandtner W, Sitte HH (2014) Evidence for a role of transporter-mediated currents in the depletion of brain serotonin induced by serotonin transporter substrates. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:1355–365 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, Rothman RB, Goldberg SR, Lupica CR, Sitte HH, Brandt SD, Telia SR, Cozzi NV, Schindler CW (2013) Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:552–562 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

