Concurrent Implantation of Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Improved Survival of Patients With Postcardiotomy Cardiogenic Shock
- PMID: 30346032
- PMCID: PMC6587979
- DOI: 10.1111/aor.13317
Concurrent Implantation of Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump and Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Improved Survival of Patients With Postcardiotomy Cardiogenic Shock
Abstract
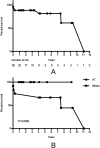
The aim of this study is to report the combined application of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) with intra-aortic balloon pumping (IABP) in postcardiotomy cardiac shock (PCS). A total of 60 consecutive patients who received both ECMO and IABP (concomitantly 24 hours) for PCS from February 2006 to March 2017 at Fuwai Hospital were included in our study. Clinical characteristics of the patients were collected retrospectively and compared between survivors and non-survivors. Logistic regression analysis was used as predictors for survival to discharge. The study cohort had a mean age of 51.4±12.7 years with 75% males. ECMO was implanted intra-operatively in 38 (63%) patients and post-operatively in 22 (37%) patients. ECMO was implanted concurrently with IABP in 38 (63%) patients. Heart transplantation (38%) and coronary artery bypass graft (33%) were the main surgical procedures. ECMO was weaned successfully in 48% patients, and the rate of survival to discharge was 43%. Survivors showed less bedside ECMO implantation (12% vs. 41%, P=0.012) and more concurrent implantation of ECMO with IABP (81% vs. 50%, P=0.014). Concurrent implantation of IABP with ECMO (OR=0.177, P=0.015, 95% CI: 0.044-0.718) was an independent predictor of survival to discharge. As for complications, the rate of renal failure (59% vs. 15%, P=0.001) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (29% vs. 0, P=0.003) was higher in patients who failed to survive to discharge. Patients who had heart transplantation had a better long-term survival than others (P=0.0358). In summary, concurrent implantation of ECMO with IABP provides better short-term outcome for PCS and combined application of ECMO with IABP for PCS after heart transplantation had a favorable long-term outcome.
Keywords: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.; Intra-aortic balloon pumping; Postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock.
© 2018 The Authors. Artificial Organs published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Center for Artificial Organ and Transplantation (ICAOT).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concurrent initiation of intra-aortic balloon pumping with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation reduced in-hospital mortality in postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock.Ann Intensive Care. 2019 Jan 23;9(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0496-9. Ann Intensive Care. 2019. PMID: 30673888 Free PMC article.
-
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation with intra-aortic balloon pump for postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Perfusion. 2023 Jan;38(1):142-149. doi: 10.1177/02676591211042568. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Perfusion. 2023. PMID: 34479456
-
Concomitant Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump Use in Cardiogenic Shock Requiring Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018 Sep;11(9):e006930. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.118.006930. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2018. PMID: 30354593
-
Effect of an intra-aortic balloon pump with venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation on mortality of patients with cardiogenic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis†.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019 Mar 1;55(3):395-404. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezy304. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30252028
-
Postcardiotomy Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation With and Without Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022 Aug;36(8 Pt B):2876-2883. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2022.02.006. Epub 2022 Feb 11. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2022. PMID: 35304046
Cited by
-
Role of acute mechanical circulatory support devices in cardiogenic shock.Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 Jul;39(Suppl 1):25-46. doi: 10.1007/s12055-023-01484-w. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 37525710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Outcomes of VA-ECMO with and without Left Centricular (LV) Decompression Using Intra-Aortic Balloon Pumping (IABP) versus Other LV Decompression Techniques: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jul 30;26:e924009. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924009. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32729556 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of VA-ECMO plus intra-aortic balloon pump for cardiac shock in patients with type A aortic dissection: a case series.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023 Oct 24;18(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02405-z. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37875966 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac intensive care management of high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention using the venoarterial ECMO support.Heart Fail Rev. 2020 Sep;25(5):833-846. doi: 10.1007/s10741-019-09862-6. Heart Fail Rev. 2020. PMID: 31677013 Review.
-
Impact of preoperative intra-aortic balloon pump on outcomes in coronary artery bypass grafting for unprotected left-main coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024 Jun 30;14(3):340-351. doi: 10.21037/cdt-23-418. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2024. PMID: 38975005 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Golding LA. Postcardiotomy mechanical support. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1991;3:29–32. - PubMed
-
- Smith C, Bellomo R, Raman JS, et al. An extracorporeal membrane oxygenation‐based approach to cardiogenic shock in an older population. Ann Thorac Surg 2001;71:1421–7. - PubMed
-
- Abrams D, Combes A, Brodie D. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in cardiopulmonary disease in adults. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:2769–78. - PubMed
-
- Ko WJ, Lin CY, Chen RJ, Wang SS, Lin FY, Chen YS. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for adult postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:538–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

