Rapid T1 quantification from high resolution 3D data with model-based reconstruction
- PMID: 30346053
- PMCID: PMC6588000
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27502
Rapid T1 quantification from high resolution 3D data with model-based reconstruction
Abstract
Purpose: Magnetic resonance imaging protocols for the assessment of quantitative information suffer from long acquisition times since multiple measurements in a parametric dimension are required. To facilitate the clinical applicability, accelerating the acquisition is of high importance. To this end, we propose a model-based optimization framework in conjunction with undersampling 3D radial stack-of-stars data.
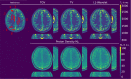
Theory and methods: High resolution 3D T1 maps are generated from subsampled data by employing model-based reconstruction combined with a regularization functional, coupling information from the spatial and parametric dimension, to exploit redundancies in the acquired parameter encodings and across parameter maps. To cope with the resulting non-linear, non-differentiable optimization problem, we propose a solution strategy based on the iteratively regularized Gauss-Newton method. The importance of 3D-spectral regularization is demonstrated by a comparison to 2D-spectral regularized results. The algorithm is validated for the variable flip angle (VFA) and inversion recovery Look-Locker (IRLL) method on numerical simulated data, MRI phantoms, and in vivo data.
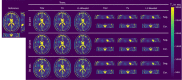
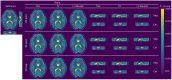
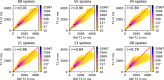
Results: Evaluation of the proposed method using numerical simulations and phantom scans shows excellent quantitative agreement and image quality. T1 maps from accelerated 3D in vivo measurements, e.g. 1.8 s/slice with the VFA method, are in high accordance with fully sampled reference reconstructions.
Conclusions: The proposed algorithm is able to recover T1 maps with an isotropic resolution of 1 mm3 from highly undersampled radial data by exploiting structural similarities in the imaging volume and across parameter maps.
Keywords: MRI; T1 quantification; constrained reconstruction; imaging; inversion-recovery Look-Locker; model-based reconstruction; variable flip angle.
© 2018 The Authors Magnetic Resonance in Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Tofts P. Quantitative MRI of the brain: measuring changes caused by disease. 2005.
-
- Stikov N, Boudreau M, Levesque IR, Tardif CL, Barral JK, Pike GB. On the accuracy of T1 mapping: searching for common ground. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:514–522. - PubMed
-
- Deoni SC, Rutt BK, Peters TM. Rapid combined T1 and T2 mapping using gradient recalled acquisition in the steady state. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:515–526. - PubMed
-
- Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P. SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1999;42:952–962. - PubMed
-
- Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, et al. Generalized Autocalibrating Partially Parallel Acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:1202–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

