Rapidly progressive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with microglial reactivity and small heat shock protein expression in reactive astrocytes
- PMID: 30346063
- PMCID: PMC7379307
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12525
Rapidly progressive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with microglial reactivity and small heat shock protein expression in reactive astrocytes
Abstract
Aims: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a chronic neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive loss of motor neurons, muscle weakness, spasticity, paralysis and death usually within 2-5 years of onset. Neuroinflammation is a hallmark of ALS pathology characterized by activation of glial cells, which respond by upregulating small heat shock proteins (HSPBs), but the exact underlying pathological mechanisms are still largely unknown. Here, we investigated the association between ALS disease duration, lower motor neuron loss, TARDNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology, neuroinflammation and HSPB expression.
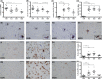
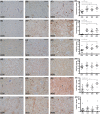
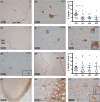
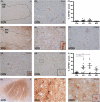
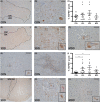
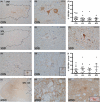
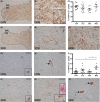
Methods: With immunohistochemistry, we examined HSPB1, HSPB5, HSPB6, HSPB8 and HSP16.2 expression in cervical, thoracic and sacral spinal cord regions in 12 ALS cases, seven with short disease duration (SDD), five with moderate disease duration (MDD), and ten age-matched controls. Expression was quantified using ImageJ to examine HSP expression, motor neuron numbers, microglial and astrocyte density and phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43+) inclusions.
Results: SDD was associated with elevated HSPB5 and 8 expression in lateral tract astrocytes, while HSP16.2 expression was increased in astrocytes in MDD cases. SDD cases had higher numbers of motor neurons and microglial activation than MDD cases, but similar levels of motor neurons with pTDP-43+ inclusions.
Conclusions: Increased expression of several HSPBs in lateral column astrocytes suggests that astrocytes play a role in the pathogenesis of ALS. SDD is associated with increased microgliosis, HSPB5 and 8 expression in astrocytes, and only minor changes in motor neuron loss. This suggests that the interaction between motor neurons, microglia and astrocytes determines neuronal fate and functional decline in ALS.
Keywords: HSPB; TDP-43 pathology; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; astrocytes; inflammation; small heat shock proteins.
© 2018 The Authors. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Neuropathological Society.
Figures
References
-
- van Es MA, Hardiman O, Chio A, Al‐Chalabi A, Pasterkamp RJ, Veldink JH, et al Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 2017; 390: 2084–98 - PubMed
-
- Berlowitz DJ, Howard ME, Fiore JFJ, Vander Hoorn S, O'Donoghue FJ, Westlake J, et al Identifying who will benefit from non‐invasive ventilation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neurone disease in a clinical cohort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2016; 87: 280–6 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

