LGI1 antibodies alter Kv1.1 and AMPA receptors changing synaptic excitability, plasticity and memory
- PMID: 30346486
- PMCID: PMC6202570
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awy253
LGI1 antibodies alter Kv1.1 and AMPA receptors changing synaptic excitability, plasticity and memory
Abstract
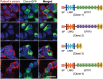
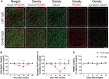
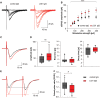
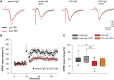
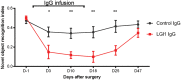
Leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 (LGI1) is a secreted neuronal protein that forms a trans-synaptic complex that includes the presynaptic disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 23 (ADAM23), which interacts with voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1, and the postsynaptic ADAM22, which interacts with AMPA receptors. Human autoantibodies against LGI1 associate with a form of autoimmune limbic encephalitis characterized by severe but treatable memory impairment and frequent faciobrachial dystonic seizures. Although there is evidence that this disease is immune-mediated, the underlying LGI1 antibody-mediated mechanisms are unknown. Here, we used patient-derived immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies to determine the main epitope regions of LGI1 and whether the antibodies disrupt the interaction of LGI1 with ADAM23 and ADAM22. In addition, we assessed the effects of patient-derived antibodies on Kv1.1, AMPA receptors, and memory in a mouse model based on cerebroventricular transfer of patient-derived IgG. We found that IgG from all patients (n = 25), but not from healthy participants (n = 20), prevented the binding of LGI1 to ADAM23 and ADAM22. Using full-length LGI1, LGI3, and LGI1 constructs containing the LRR1 domain (EPTP1-deleted) or EPTP1 domain (LRR3-EPTP1), IgG from all patients reacted with epitope regions contained in the LRR1 and EPTP1 domains. Confocal analysis of hippocampal slices of mice infused with pooled IgG from eight patients, but not pooled IgG from controls, showed a decrease of total and synaptic levels of Kv1.1 and AMPA receptors. The effects on Kv1.1 preceded those involving the AMPA receptors. In acute slice preparations of hippocampus, patch-clamp analysis from dentate gyrus granule cells and CA1 pyramidal neurons showed neuronal hyperexcitability with increased glutamatergic transmission, higher presynaptic release probability, and reduced synaptic failure rate upon minimal stimulation, all likely caused by the decreased expression of Kv1.1. Analysis of synaptic plasticity by recording field potentials in the CA1 region of the hippocampus showed a severe impairment of long-term potentiation. This defect in synaptic plasticity was independent from Kv1 blockade and was possibly mediated by ineffective recruitment of postsynaptic AMPA receptors. In parallel with these findings, mice infused with patient-derived IgG showed severe memory deficits in the novel object recognition test that progressively improved after stopping the infusion of patient-derived IgG. Different from genetic models of LGI1 deficiency, we did not observe aberrant dendritic sprouting or defective synaptic pruning as potential cause of the symptoms. Overall, these findings demonstrate that patient-derived IgG disrupt presynaptic and postsynaptic LGI1 signalling, causing neuronal hyperexcitability, decreased plasticity, and reversible memory deficits.
Figures



Comment in
-
Pre- and postsynaptic effects of LGI1 autoantibodies in a murine model of limbic encephalitis.Brain. 2018 Nov 1;141(11):3092-3095. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy271. Brain. 2018. PMID: 30364979 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

