Nanothermometry Reveals Calcium-Induced Remodeling of Myosin
- PMID: 30346792
- PMCID: PMC6818504
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02989
Nanothermometry Reveals Calcium-Induced Remodeling of Myosin
Abstract
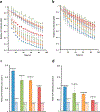
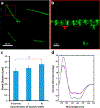
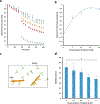
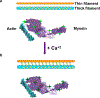
Ions greatly influence protein structure-function and are critical to health and disease. A 10, 000-fold higher calcium in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of muscle suggests elevated calcium levels near active calcium channels at the SR membrane and the impact of localized high calcium on the structure-function of the motor protein myosin. In the current study, combined quantum dot (QD)-based nanothermometry and circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy enabled detection of previously unknown enthalpy changes and associated structural remodeling of myosin, impacting its function following exposure to elevated calcium. Cadmium telluride QDs adhere to myosin, function as thermal sensors, and reveal that exposure of myosin to calcium is exothermic, resulting in lowering of enthalpy, a decrease in alpha helical content measured using CD spectroscopy, and the consequent increase in motor efficiency. Isolated muscle fibers subjected to elevated levels of calcium further demonstrate fiber lengthening and decreased motility of actin filaments on myosin-functionalized substrates. Our results, in addition to providing new insights into our understanding of muscle structure-function, establish a novel approach to understand the enthalpy of protein-ion interactions and the accompanying structural changes that may occur within the protein molecule.
Keywords: Quantum dot thermometry; calcium; molecular motor myosin; muscle function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
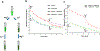
References
-
- Gordon AM; Homsher E; Regnier M Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol. Rev 2000, 80, 853–924. - PubMed
-
- Linari M; et al. Force generation by skeletal muscle is controlled by mechanosensing in myosin filaments. Nature 2015, 528, 276–279. - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima C How Ca2+-ATPase pumps ions across the sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res 2009, 1793 (6), 941. - PubMed
-
- Huxley HE; Brown W The low-angle x-ray diagram of vertebrate striated muscle and its behaviour during contraction and rigor. J. Mol. Biol 1967, 30, 383–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

