Multisite study of the relationships between antemortem [11C]PIB-PET Centiloid values and postmortem measures of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology
- PMID: 30347188
- PMCID: PMC6368897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.09.001
Multisite study of the relationships between antemortem [11C]PIB-PET Centiloid values and postmortem measures of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology
Abstract
Introduction: We sought to establish the relationships between standard postmortem measures of AD neuropathology and antemortem [11C]PIB-positron emission tomography ([11C]PIB-PET) analyzed with the Centiloid (CL) method, a standardized scale for Aβ-PET quantification.
Methods: Four centers contributed 179 participants encompassing a broad range of clinical diagnoses, PET data, and autopsy findings.
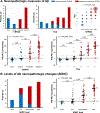
Results: CL values increased with each CERAD neuritic plaque score increment (median -3 CL for no plaques and 92 CL for frequent plaques) and nonlinearly with Thal Aβ phases (increases were detected starting at phase 2) with overlap between scores/phases. PET-pathology associations were comparable across sites and unchanged when restricting the analyses to the 56 patients who died within 2 years of PET. A threshold of 12.2 CL detected CERAD moderate-to-frequent neuritic plaques (area under the curve = 0.910, sensitivity = 89.2%, specificity = 86.4%), whereas 24.4 CL identified intermediate-to-high AD neuropathological changes (area under the curve = 0.894, sensitivity = 84.1%, specificity = 87.9%).
Discussion: Our study demonstrated the robustness of a multisite Centiloid [11C]PIB-PET study and established a range of pathology-based CL thresholds.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease neuropathologic changes; CERAD; Centiloid; Harmonization; Neuropathology; Pittsburgh compound-B; Positron emission tomography; Thal; Threshold; β-amyloid.
Copyright © 2018 the Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
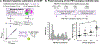

References
-
- Johnson KA, Minoshima S, Bohnen NI, Donohoe KJ, Foster NL, Herscovitch P, et al. Appropriate use criteria for amyloid PET: a report of the Amyloid Imaging Task Force, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimers Dement J Alzheimers Assoc 2013;9:e-1–16. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.01.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054076/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG053435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027859/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021028/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG031563/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG045611/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG025204/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041851/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG045333/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG056366/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG038791/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054449/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG058676/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011378/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG012435/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032306/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005133/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG031861/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG025516/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS097495/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States

