Detection of human rhinoviruses by reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification method (RT-SIBA)
- PMID: 30347198
- PMCID: PMC7113843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2018.10.015
Detection of human rhinoviruses by reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification method (RT-SIBA)
Abstract
Background: Rhinovirus (RV), a major cause of respiratory infection in humans, imposes an enormous economic burden due to the direct and indirect costs associated with the illness. Accurate and timely diagnosis is crucial for deciding the appropriate clinical approach and minimizing unnecessary prescription of antibiotics. Diagnosis of RV is extremely challenging due to genetic and serological variability among its numerous types and their similarity to enteroviruses.
Objective: We sought to develop a rapid nucleic acid test that can be used for the detection of Rhinovirus within both laboratory and near patient settings.
Study design: We developed and evaluated a novel isothermal nucleic acid amplification method called Reverse Transcription Strand Invasion-Based Amplification (RT-SIBA) to rapidly detect Rhinovirus from clinical specimens.
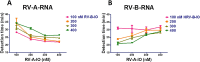
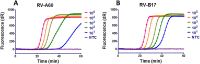
Result: The method, RT-SIBA, detected RV in clinical specimens with high analytical sensitivity (96%) and specificity (100%). The time to positive result was significantly shorter for the RV RT-SIBA assay than for a reference RV nucleic acid amplification method (RT-qPCR).
Conclusion: The rapid detection time of the RV SIBA assay, as well as its compatibility with portable instruments, will facilitate prompt diagnosis of infection and thereby improve patient care.
Keywords: Amplification; Diagnostics; Isothermal; Point-of-care; RT-SIBA; Rhinovirus; Virus.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification (RT-SIBA): a method for rapid detection of influenza A and B.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Jun;100(12):5559-67. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7491-y. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27063012 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the reverse transcription strand invasion based amplification (RT-SIBA) RSV assay, a rapid molecular assay for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Sep;95(1):55-58. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31160164
-
Rapid and sensitive real-time assay for the detection of respiratory syncytial virus using RT-SIBA®.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Feb 10;17(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2227-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28183291 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the detection of respiratory virus infection in humans.J Med Virol. 2020 Apr;92(4):408-417. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25674. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 31944312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging molecular assays for detection and characterization of respiratory viruses.Clin Lab Med. 2009 Dec;29(4):673-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2009.07.005. Clin Lab Med. 2009. PMID: 19892228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of real-time fluorescent reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for rhinovirus detection.J Med Virol. 2019 Jul;91(7):1232-1238. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25427. Epub 2019 Feb 22. J Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 30735248 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Different Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction-Based Methods for Wastewater Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2: Exploratory Study.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Aug 19;10:e53175. doi: 10.2196/53175. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39158943 Free PMC article.
-
Viral etiology and atopic characteristics in high-risk asthmatic children hospitalized for lower respiratory tract infection.Transl Pediatr. 2020 Aug;9(4):541-550. doi: 10.21037/tp-20-165. Transl Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32953552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buissonnière A., Bénéjat L., Charron P., Bessède E., Lehours P., Valdenaire G. A new kit to detect Campylobacter species in stool specimens: the Orion GenRead Campylobacter®. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018;37(8):1585–1587. - PubMed
-
- Dagher H., Donninger H., Hutchinson P., Ghildyal R., Bardin P. Rhinovirus detection: comparison of real-time and conventional PCR. J. Virol. Methods. 2004;117:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Eboigbodin K.E., Brummer M., Ojalehto T., Hoser M. Rapid molecular diagnostic test for Zika virus with low demands on sample preparation and instrumentation. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016;86:369–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

