Poor between-session recall of extinction learning and hippocampal activation and connectivity in children
- PMID: 30347237
- PMCID: PMC6286149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.10.007
Poor between-session recall of extinction learning and hippocampal activation and connectivity in children
Abstract
Background: In healthy adults, successful between-session recall of extinction learning depends on the hippocampus and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC), especially when tested in the extinction context. Poor extinction recall and dysfunction within hippocampal-vmPFC circuitry are associated with fear-based disorders (e.g., anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder). Despite the early age of onset of virtually all fear-based disorders and the protracted development of the hippocampus and vmPFC across the first two decades of life, little is known about extinction recall and the underlying neural correlates in children.
Methods: Here, we tested extinction recall in 43 pre-adolescent children (ages 6-11 yrs) by coupling functional magnetic resonance imaging and virtual reality with a novel interpersonal threat-related two-day (ABBA) fear-extinction paradigm. Conditioned fear responding was assessed at behavioral, subjective, physiological, and neural levels.
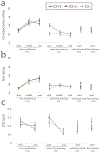
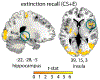
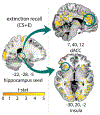
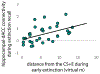
Results: Although children demonstrated intact within-session extinction, there was poor between-session recall of extinction learning (retention index: 13.56%), evidenced by elevations in skin conductance, avoidant behavioral responses, and subjective ratings. Elevations in conditioning fear responding were accompanied by activation in the hippocampus and insula, and increased connectivity of the hippocampus with the insula and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex - regions implicated in the return of fear in adult studies. Children who kept more distance from the extinguished cue during extinction subsequently demonstrated heightened hippocampal-cingulate coupling during recall, suggesting that avoidant behavior interferes with extinction retention.
Conclusions: Poor extinction recall in children may have implications for developmental vulnerability to fear-based disorders, and for the application of therapeutic strategies that rely on principles of extinction (e.g., exposure therapy) to pediatric samples.
Keywords: Anterior cingulate cortex; Context; Extinction retention; Fear learning; Insula; fMRI.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
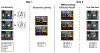
References
-
- Craig AD (2009). How do you feel — now? The anterior insula and human awareness. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(1), 59–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2555 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Åhs F, Kragel PA, Zielinski DJ, Brady R, & LaBar KS (2015). Medial prefrontal pathways for the contextual regulation of extinguished fear in humans. NeuroImage, 122, 262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.07.051 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker KD, & Richardson R (2015). Forming competing fear learning and extinction memories in adolescence makes fear difficult to inhibit. Learning & Memory, 22, 537–543. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.039487.114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beckers T, Krypotos A-M, Boddez Y, Effting M, & Kindt M (2013). What’s wrong with fear conditioning? Biological Psychology, 92(1), 90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.12.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blankenship SL, Redcay E, Dougherty LR, & Riggins T (2017). Development of hippocampal functional connectivity during childhood. Human Brain Mapping, 38(1), 182–201. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23353 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

