Unfractionated and Low Molecular Weight Heparin Reduce Platelet Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer Cells
- PMID: 30347648
- PMCID: PMC6222876
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102690
Unfractionated and Low Molecular Weight Heparin Reduce Platelet Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
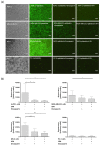
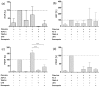
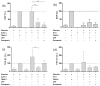
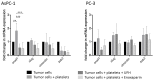
The interaction with platelets is of crucial importance for tumor cells passing through hematogenous metastasis. Platelets protect cancer cells from immune surveillance and exhibit many other prometastatic effects. Notably, platelets can change the epithelial tumor phenotype, a process termed epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which confers stem cell-like properties onto tumor cells associated with an increased motility and drug resistance. The aim of the study is to investigate the impact of heparin on the platelet induced EMT program in pancreatic and prostate tumor cells. Platelet activation and interaction with cancer cells were determined by static adhesion assays. Applying ELISAs, the platelet release of EMT inducing mediators was quantified. EMT marker protein expression by tumor cells was explored by western blot and qPCR. Our data show that different tumor cell entities have different platelet binding capacities and also that a weak interaction is sufficient to change tumor cell phenotype. Additionally, unfractionated heparin (UFH) as well as low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) reduced tumor cell platelet interaction. Subsequently, attenuated platelet-derived mediator release resulted in reduced EMT marker protein and transcription factor expression by the cancer cells and decreased cell migration. These data suggest that heparin reduces platelet induced EMT program and prevents the formation of cancer cells with stem cell-like properties. This additional mechanism argues for the use of heparin in oncological applications.
Keywords: EMT; cancer stem cells; enoxaparin; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; heparin; platelet; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Low Molecular Weight Heparin Tinzaparin Attenuates Platelet Activation in Terms of Metastatic Niche Formation by Coagulation-Dependent and Independent Pathways.Molecules. 2018 Oct 24;23(11):2753. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112753. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30356007 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosaminoglycans as Tools to Decipher the Platelet Tumor Cell Interaction: A Focus on P-Selectin.Molecules. 2020 Feb 26;25(5):1039. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051039. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32110917 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rb prevents the metastasis of hepatocarcinoma by blocking the platelet-tumor cell interaction.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;398(2):1721-1733. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03387-y. Epub 2024 Aug 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39172150
-
The role of tumor-platelet interplay and micro tumor thrombi during hematogenous tumor metastasis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Jun;46(3):521-532. doi: 10.1007/s13402-023-00773-1. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 36652166 Review.
-
The crossroads of adenosinergic pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 2):202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.06.012. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35779713 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelets involved tumor cell EMT during circulation: communications and interventions.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Jun 3;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00887-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35659308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introduction to the Molecules Special Edition Entitled 'Heparan Sulfate and Heparin: Challenges and Controversies': Some Outstanding Questions in Heparan Sulfate and Heparin Research.Molecules. 2019 Apr 10;24(7):1399. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071399. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30974725 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Platelet Count Correlates With Postoperative Perineural Invasion on Specimen in Patients Treated With Radical Prostatectomy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 7;12:906936. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.906936. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35747816 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Opportunities Associated With Platelets in Pancreatic Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 12;12:850485. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.850485. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35494001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs Orchestrate Pathophysiology of Breast Cancer Brain Metastasis: Advances in Therapy.Mol Cancer. 2020 Feb 15;19(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-1140-x. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32059676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Labelle M., Hynes R.O. The initial hours of metastasis: The importance of cooperative host-tumor cell interactions during hematogenous dissemination. Cancer Discov. 2012;2:1091–1099. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0329. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nieswandt B., Hafner M., Echtenacher B., Männel D.N. Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 1999;59:1295–1300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

