Anti-Angiogenic miR-222, miR-195, and miR-21a Plasma Levels in T1DM Are Improved by Metformin Therapy, Thus Elucidating Its Cardioprotective Effect: The MERIT Study
- PMID: 30347712
- PMCID: PMC6214022
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103242
Anti-Angiogenic miR-222, miR-195, and miR-21a Plasma Levels in T1DM Are Improved by Metformin Therapy, Thus Elucidating Its Cardioprotective Effect: The MERIT Study
Abstract
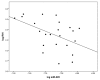
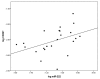
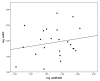
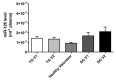
Type 1 diabetes (T1DM) is associated with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) and reduced life expectancy. We thus hypothesized that anti-angiogenic miRs are increased in T1DM, and the cardioprotective effect of metformin is mediated via reducing those miRs. In an open label, case-controlled study, 23 T1DM patients without CVD were treated with metformin for eight weeks (TG), matched with nine T1DM patients on standard treatment (SG) and 23 controls (CG). Plasma miR-222, miR-195, miR-21a and miR-126 were assayed by real-time RT-qPCR. The results were correlated with: endothelial function (RHI), circulating endothelial progenitor cells (cEPCs) (vascular repair marker, CD45dimCD34⁺VEGFR2⁺ cells) and circulating endothelial cells (cECs) (vascular injury marker, CD45dimCD34⁺CD133⁻CD144⁺ cells). miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a were higher in T1DM than CG; p = 0.009, p < 0.0001, p = 0.0001, respectively. There was an inverse correlation between logmiR-222 and logRHI (p < 0.05) and a direct correlation between logmiR-222 and logCD34⁺ (p < 0.05) in TG. Metformin reduced miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a levels in TG; p = 0.007, p = 0.002 p = 0.0012, respectively. miRs remained unchanged in SG. miR-126 was similar in all groups. There was a positive association between changes in logmiR-222 and logcECs after metformin in TG (p < 0.05). Anti-angiogenic miRs are increased in T1DM. Metformin has cardioprotective effects through downregulating miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a, beyond improving glycemic control.
Keywords: T1DM; anti-angiogenic; metformin; miRs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metformin improves circulating endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in type 1 diabetes: MERIT study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016 Aug 26;15(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0413-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 27561827 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of miR-342 in Vascular Health. Study in Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease in Mononuclear Cells, Plasma, Inflammatory Cytokines and PANX2.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 29;21(19):7217. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197217. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33003647 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated anti-angiogenic miR-424-5p in type 1 diabetes (model of subclinical cardiovascular disease) correlates with endothelial progenitor cells, CXCR1/2 and other parameters of vascular health.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 14;12(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02332-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33985567 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular and metabolic effects of metformin added to insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020 Sep;36(6):e3334. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3334. Epub 2020 May 26. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32390336
-
Insulin resistance, role of metformin and other non-insulin therapies in pediatric type 1 diabetes.Pediatr Diabetes. 2016 Dec;17(8):545-558. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12337. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Pediatr Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 26592507 Review.
Cited by
-
Micro-RNA Implications in Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 10;22(22):12165. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212165. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic performance of new and classic CSF biomarkers in age-related dementias.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Apr 27;11(8):2420-2429. doi: 10.18632/aging.101925. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31029057 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of miR-199b-5p in Colony Forming Unit-Hill's Colonies Positively Mediates the Inflammatory Response in Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease Model: Metformin Therapy Attenuates Its Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8087. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158087. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125657 Free PMC article.
-
Current Insights into miRNA and lncRNA Dysregulation in Diabetes: Signal Transduction, Clinical Trials and Biomarker Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 14;15(10):1269. doi: 10.3390/ph15101269. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metformin's effect on metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease through the miR-200a-5p and AMPK/SERCA2b pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 17;15:1477212. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1477212. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39741625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piccolo R., Galasso G., Iversen A.Z., Eitel I., Dominguez-Rodriguez A., Gu Y.L., de Smet B.J., Mahmoud K.D., Abreu-Gonzalez P., Trimarco B., et al. Effects of baseline coronary occlusion and diabetes mellitus in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014;114:1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.07.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petrie J.R., Chaturvedi N., Ford I., Brouwers M., Greenlaw N., Tillin T., Hramiak I., Hughes A.D., Jenkins A.J., Klein B.E.K., et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in patients with type 1 diabetes (REMOVAL): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:597–609. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30194-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

