Anti-Angiogenic miR-222, miR-195, and miR-21a Plasma Levels in T1DM Are Improved by Metformin Therapy, Thus Elucidating Its Cardioprotective Effect: The MERIT Study
- PMID: 30347712
- PMCID: PMC6214022
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19103242
Anti-Angiogenic miR-222, miR-195, and miR-21a Plasma Levels in T1DM Are Improved by Metformin Therapy, Thus Elucidating Its Cardioprotective Effect: The MERIT Study
Abstract
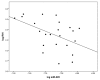
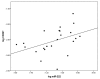
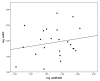
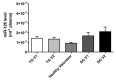
Type 1 diabetes (T1DM) is associated with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) and reduced life expectancy. We thus hypothesized that anti-angiogenic miRs are increased in T1DM, and the cardioprotective effect of metformin is mediated via reducing those miRs. In an open label, case-controlled study, 23 T1DM patients without CVD were treated with metformin for eight weeks (TG), matched with nine T1DM patients on standard treatment (SG) and 23 controls (CG). Plasma miR-222, miR-195, miR-21a and miR-126 were assayed by real-time RT-qPCR. The results were correlated with: endothelial function (RHI), circulating endothelial progenitor cells (cEPCs) (vascular repair marker, CD45dimCD34⁺VEGFR2⁺ cells) and circulating endothelial cells (cECs) (vascular injury marker, CD45dimCD34⁺CD133⁻CD144⁺ cells). miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a were higher in T1DM than CG; p = 0.009, p < 0.0001, p = 0.0001, respectively. There was an inverse correlation between logmiR-222 and logRHI (p < 0.05) and a direct correlation between logmiR-222 and logCD34⁺ (p < 0.05) in TG. Metformin reduced miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a levels in TG; p = 0.007, p = 0.002 p = 0.0012, respectively. miRs remained unchanged in SG. miR-126 was similar in all groups. There was a positive association between changes in logmiR-222 and logcECs after metformin in TG (p < 0.05). Anti-angiogenic miRs are increased in T1DM. Metformin has cardioprotective effects through downregulating miR-222, miR-195 and miR-21a, beyond improving glycemic control.
Keywords: T1DM; anti-angiogenic; metformin; miRs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Piccolo R., Galasso G., Iversen A.Z., Eitel I., Dominguez-Rodriguez A., Gu Y.L., de Smet B.J., Mahmoud K.D., Abreu-Gonzalez P., Trimarco B., et al. Effects of baseline coronary occlusion and diabetes mellitus in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014;114:1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.07.030. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Petrie J.R., Chaturvedi N., Ford I., Brouwers M., Greenlaw N., Tillin T., Hramiak I., Hughes A.D., Jenkins A.J., Klein B.E.K., et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in patients with type 1 diabetes (REMOVAL): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5:597–609. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30194-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

