Investigation of the In Vivo Metabolism of Sibirioside A and Angoroside C in Rats by HPLC-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn
- PMID: 30347747
- PMCID: PMC6222638
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102702
Investigation of the In Vivo Metabolism of Sibirioside A and Angoroside C in Rats by HPLC-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn
Abstract
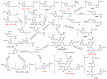
Sibirioside A and angoroside C are two important phenylpropanoid glycosides of the traditional Chinese medicine Scrophulariae Radix. High performance liquid chromatography, coupled with an ion trap time-of-flight multistage mass spectrometry equipped with electrospray ionization source (HPLC-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn), was applied to the profile and we identified the metabolites of sibirioside A and angoroside C in vivo in rats. A total of four metabolites of sibirioside A were identified: SM1, SM2 and SM3 which were known as new compounds. A total of 25 metabolites were detected for angoroside C: AM4, AM5, AM6, AM7, AM16, AM17, AM20, AM21, AM22, AM23 and AM25 which were identified to be new compounds. The main metabolic reactions were hydrolysis, reduction, hydroxylation, methylation, sulfation, and gluconylation. The prototype of sibirioside A was widely distributed in tissues found in the heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, stomach and small intestine of rats, and mainly distributed in the stomach, small intestine, kidney and liver. But for angoroside C, nothing was found in the viscera except the stomach and small intestine. The metabolites of sibirioside A were mainly eliminated from feces, while it was urine for the metabolites of angoroside C. Furthermore, 19 metabolites were likely to have bioactivities based on the 'PharmMapper' analysis, which roughly matched the known pharmacological activities of Scrophulariae Radix (SR) and the prototypes. One of the main pharmacological activities of SR in traditional Chinese medicine is anti-diabetes, and the predicted results showed that SM1, SM2, SM3, AM2, AM4, AM5, AM6, AM9, AM10, AM11, AM12, AM13, AM15, AM18, AM19, AM24, and AM25 might be used to cure diabetes. These findings provide a reference for studying the metabolism, distribution and pharmacological actions of phenylpropanoid glycosides in vivo.
Keywords: HPLC-IT-TOF-MSn; Scrophulariae Radix; angoroside C; metabolism; sibirioside A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Xu F.Q., Xu X.D., Chen S.L. Progress in chemical constituents and bioactivities of Scrophularia ningpoensis. Mod. Chin. Med. 2013;9:752–759.
-
- Li Y.M., Zeng H.W., He X., Jiang Y.Y., Jiang S.H., Zhu D.Y. Iridoid and phenylpropanoid glycosides of Scrophularia ningpoensis inhibit the formation of LTB4 and platelet aggregation. Acad. J. Second Mil. Med. Univ. 1999;20:301–303.
-
- Liu H., Zheng Y.F., Li C.Y., Zheng Y.Y., Wang D.Q., Wu Z., Huang L., Wang Y.G., Li P.B., Peng W., et al. Discovery of Anti-inflammatory Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Formula Kouyanqing Granule based on Relevance Analysis between Chemical Characters and Biological Effects. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:18080. doi: 10.1038/srep18080. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y.M., Han Z.H., Jiang S.H., Yao S.D., Zhu D.Y. Fast repairing of oxidized OH radical adducts of dAMP and dGMP by phenylpropanoid glycosides from Scrophularia ningpoensis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2000;21:1125–1128. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

