Mediterranean Lifestyle in Relation to Cognitive Health: Results from the HELIAD Study
- PMID: 30347812
- PMCID: PMC6213445
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10101557
Mediterranean Lifestyle in Relation to Cognitive Health: Results from the HELIAD Study
Abstract
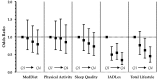
Many lifestyle factors have been linked to cognitive function but little is known about their combined effect. An overall lifestyle pattern for people living in the Mediterranean basin has been proposed, including diet, but also physical activity, sleep and daily living activities with social/intellectual aspects. We aimed to examine the associations between a combination of these lifestyle factors and detailed cognitive performance. A total of 1716 participants from the Hellenic Longitudinal Investigation of Ageing and Diet (HELIAD), a population-based study of participants ≥65 years, were included in this analysis. Lifestyle factors were evaluated using standard, validated questionnaires and a Total Lifestyle Index (TLI) was constructed. Cognitive outcomes included mild cognitive impairment (MCI) diagnosis, a composite z-score (either continuous or with a threshold at the 25th percentile) and z-scores for five cognitive domains. A higher TLI was associated with 65% reduced odds for MCI in the non-demented individuals and 43% reduced odds for low global cognition when MCI participants were excluded, a risk reduction equivalent to 9 and 2.7 fewer years of ageing, respectively. Each lifestyle factor was differentially associated with domain-specific cognitive performance. Our results suggest that a TLI, more so than single lifestyle parameters, may be related to cognitive performance.
Keywords: brain health; cognition; dietary patterns; instrumental activities of daily living; lifestyle; nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, Key Findings and Advance Tables. [(accessed on 11 June 2018)]; Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/publications/files/wpp2017_keyfindings.pdf.
-
- Pusswald G., Tropper E., Kryspin-Exner I., Moser D., Klug S., Auff E., Dal-Bianco P., Lehrner J. Health-related quality of life in patients with subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment and its relation to activities of daily living. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015;47:479–486. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150284. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

