Prevalence of Low Back Pain and Dorsalgia and Associated Factors among Casual Dockworkers
- PMID: 30347825
- PMCID: PMC6210083
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph15102310
Prevalence of Low Back Pain and Dorsalgia and Associated Factors among Casual Dockworkers
Abstract
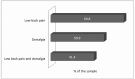
This study's aim was to analyse the relationship between musculoskeletal disorders (low back pain and dorsalgia) and sociodemographic characteristics, workload and occupational hazards among casual dockworkers. This cross-sectional study addressed casual dockworkers from the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The convenience sample was composed of 232 casual dockworkers. Data were collected using a structured interview and observation. Poisson regression analysis was used. Association between low back pain and physiological occupational risk (p = 0.006), total exertion levels (p = 0.014) and frustration (p = 0.020) remained statistically significant, while the use of illicit drugs (p = 0.023), being a quayside worker (p = 0.021) and physiological occupational risk (p = 0.040) remained associated with dorsalgia. Decreasing these variables in the workplace may also reduce the prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders such as low back pain and dorsalgia.
Keywords: casual dockworkers; musculoskeletal disorders; occupational health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prevalence of musculoskeletal diseases among casual dock workers.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2012 Mar-Apr;20(2):243-50. doi: 10.1590/s0104-11692012000200005. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2012. PMID: 22699723 English, Portuguese, Spanish.
-
The Use of Illegal Drugs and Infectious Contagious Diseases: Knowledge and Intervention among Dockworkers.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016 Jan 12;13(1):125. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13010125. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26771625 Free PMC article.
-
Musculoskeletal disorders and their influence on the quality of life of the dockworker: A cross-sectional study.Work. 2016 Feb 15;53(4):805-12. doi: 10.3233/WOR-162249. Work. 2016. PMID: 26890589
-
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders in dockworkers. Systematic review and meta-analysis.Work. 2024;79(2):585-600. doi: 10.3233/WOR-230666. Work. 2024. PMID: 38607782
-
Workplace risk factors and occupational musculoskeletal disorders, Part 1: A review of biomechanical and psychophysical research on risk factors associated with low-back pain.AIHAJ. 2000 Jan-Feb;61(1):39-50. AIHAJ. 2000. PMID: 10772613 Review.
Cited by
-
Port Workers' Use of Medical Services in a Maritime Container Terminal in Costa Rica.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 8;20(2):1124. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021124. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36673879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNCTAD United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. [(accessed on 31 May 2018)]; Available online: http://unctad.org/en/PublicationsLibrary/rmt2017_en.pdf.
-
- NTC National Transport Confederation. [(accessed on 16 October 2018)]; Available online: http://cms.cnt.org.br/Imagens%20CNT/Site%202015/Pesquisas%20PDF/Transpor....
-
- Brazil Law, No. 12.815, 5 June 2013. Provides Informations about Direct and Indirect Exploitation by the Ports Union and Port Facilities and Activities Performed by Port Operators. DiárioOficial da União: Brasília, DF, Brazil, [(accessed on 31 May 2018)];2013 Available online: http://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/_ato2011-2014/2013/lei/l12815.htm.
-
- La Torre G., Sestili C., Mannocci A., Sinopoli A., De Paolis M., De Francesco S., De Giusti M. Association between Work Related Stress and Health Related Quality of Life: The Impact of Socio-Demographic Variables. A Cross Sectional Study in a Region of Central Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018;15:159. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15010159. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical