A High-Content Screening Assay for the Discovery of Novel Proteasome Inhibitors from Formosan Soft Corals
- PMID: 30347865
- PMCID: PMC6213913
- DOI: 10.3390/md16100395
A High-Content Screening Assay for the Discovery of Novel Proteasome Inhibitors from Formosan Soft Corals
Abstract
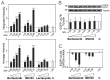
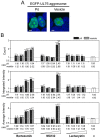
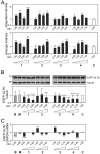
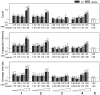
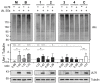
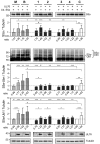
The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is a major proteolytic pathway that safeguards protein homeostasis. The main 26S proteasome consists of a 20S catalytic core proteasome and a 19S substrate recognition proteasome. UPS dysfunction underlies many important clinical diseases involving inflammation, tumors, and neurodegeneration. Currently, three 20S proteasome inhibitors, bortezomib, carfilzomib, and ixazomib, have been approved for the treatment of multiple myeloma. We aim to screen UPS inhibitors for biomedical purposes. The protein interaction network of human cytomegalovirus UL76 targets UPS, resulting in aggregations of ubiquitinated proteins termed aggresomes. In this study, we demonstrated that cell-based high-content measurements of EGFP-UL76 aggresomes responded to bortezomib and MG132 treatment in a dose-dependent manner. Employing this high-content screening (HCS) assay, we screened natural compounds purified from Formosan soft corals. Four cembrane-based compounds, sarcophytonin A (1), sarcophytoxide (2), sarcophine (3), and laevigatol A (4), were found to enhance the high-content profiles of EGFP-UL76 aggresomes with relative ratios of 0.2. By comparison to the mechanistic action of proteasome inhibitors, compounds 1 and 3 modulated the accumulation of ubiquitinated proteins, with a unique pattern likely targeting 19S proteasome. We confirmed that the EGFP-UL76 aggresome-based HCS system greatly improves the efficacy and sensitivity of the identification of proteasome inhibitors.
Keywords: cembrane; high-content screening; proteasome inhibitor; soft coral.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin-Proteasome Modulating Dolabellanes and Secosteroids from Soft Coral Clavularia flava.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jan 3;18(1):39. doi: 10.3390/md18010039. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31947850 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of Natural Proteasome Inhibitors as Novel Anticancer Therapeutics: Current Status and Perspectives.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018 Feb 13;19(4):358-367. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666170111121856. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 28079010 Review.
-
Cell-based screening of extracts of natural sources to search for inhibitors of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and identification of proteasome inhibitors from the fungus Remotididymella sp.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022 Mar 1;59:128566. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2022.128566. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35063633
-
Applied techniques for mining natural proteasome inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1843(1):26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.01.017. Epub 2013 Jan 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23360979 Review.
-
Search for Inhibitors of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System from Natural Sources for Cancer Therapy.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016;64(2):112-8. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c15-00768. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 26833439 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Marine Chemical Ecology Research on the Discovery and Development of New Pharmaceuticals.Mar Drugs. 2023 Mar 9;21(3):174. doi: 10.3390/md21030174. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36976223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update.Mar Drugs. 2018 Nov 26;16(12):467. doi: 10.3390/md16120467. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30486251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Compounds as Protease Inhibitors in Therapeutic Focus on Cancer Therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024;24(16):1167-1181. doi: 10.2174/0118715206303964240708095110. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38988167 Review.
-
Ubiquitin-Proteasome Modulating Dolabellanes and Secosteroids from Soft Coral Clavularia flava.Mar Drugs. 2020 Jan 3;18(1):39. doi: 10.3390/md18010039. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31947850 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Inhibitors from Gorgonians and Soft Corals.Mar Drugs. 2023 Jan 31;21(2):104. doi: 10.3390/md21020104. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 36827145 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Quinn R.A., Vermeij M.J., Hartmann A.C., Galtier d’Auriac I., Benler S., Haas A., Quistad S.D., Lim Y.W., Little M., Sandin S., et al. Metabolomics of reef benthic interactions reveals a bioactive lipid involved in coral defence. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016;283:20160469. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.0469. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lehmann G., Udasin R.G., Livneh I., Ciechanover A. Identification of UBact, a ubiquitin-like protein, along with other homologous components of a conjugation system and the proteasome in different gram-negative bacteria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017;483:946–950. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.037. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

