Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Potential Therapeutic Role in Cardiovascular System Disorders-A Review
- PMID: 30347877
- PMCID: PMC6213446
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10101561
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Potential Therapeutic Role in Cardiovascular System Disorders-A Review
Abstract
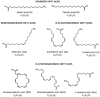
Cardiovascular diseases are described as the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in modern societies. Therefore, the importance of cardiovascular diseases prevention is widely reflected in the increasing number of reports on the topic among the key scientific research efforts of the recent period. The importance of essential fatty acids (EFAs) has been recognized in the fields of cardiac science and cardiac medicine, with the significant effects of various fatty acids having been confirmed by experimental studies. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are considered to be important versatile mediators for improving and maintaining human health over the entire lifespan, however, only the cardiac effect has been extensively documented. Recently, it has been shown that omega-3 fatty acids may play a beneficial role in several human pathologies, such as obesity and diabetes mellitus type 2, and are also associated with a reduced incidence of stroke and atherosclerosis, and decreased incidence of cardiovascular diseases. A reasonable diet and wise supplementation of omega-3 EFAs are essential in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases prevention and treatment.
Keywords: alpha-linoleic acid (ALA); cardiovascular system; docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); lipids; nutrition; omega-3 fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolism, and significance - A review.Life Sci. 2018 Jun 15;203:255-267. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.04.049. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29715470 Review.
-
Dietary n-6 and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: from biochemistry to clinical implications in cardiovascular prevention.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Mar 15;77(6):937-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.10.020. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19022225 Review.
-
Eicosapentaenoic Acid Versus Docosahexaenoic Acid as Options for Vascular Risk Prevention: A Fish Story.Am J Ther. 2016 May-Jun;23(3):e905-10. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000165. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 25828517 Review.
-
Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) from genesis to senescence: the influence of LCPUFA on neural development, aging, and neurodegeneration.Prog Lipid Res. 2014 Jan;53:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Prog Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 24334113 Review.
-
A novel, multi-ingredient supplement to manage elevated blood lipids in patients with no evidence of cardiovascular disease: a pilot study.Altern Ther Health Med. 2014 Sep-Oct;20(5):18-23. Altern Ther Health Med. 2014. PMID: 25141367 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effect of Linoleic Acid on Cholesterol Levels in a High-Fat Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 30;13(1):53. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010053. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36676979 Free PMC article.
-
Can Bioactive Food Substances Contribute to Cystic Fibrosis-Related Cardiovascular Disease Prevention?Nutrients. 2023 Jan 8;15(2):314. doi: 10.3390/nu15020314. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untargeted Metabolomics Combined with Sensory Analysis to Evaluate the Chemical Changes in Coppa Piacentina PDO during Different Ripening Times.Molecules. 2023 Feb 27;28(5):2223. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052223. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903465 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid profile and safety aspects of the edible oil prepared by artisans' at small-scale agricultural companies.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Aug 8;9(10):5402-5414. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2495. eCollection 2021 Oct. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34646511 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating lipidomics and genomics: emerging tools to understand cardiovascular diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Mar;78(6):2565-2584. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03715-4. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33449144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bodkowski R., Patkowska-Sokola B., Filip-Psurska B., Kempinska K., Wietrzyk J., Czyz K., Walisiewicz-Niedbalska W., Usydus Z. Evaluation of the anti-proliferative activity of natural lipid preparations against tumor cell lines. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2014;13:257–266.
-
- Smith S., Ralston J., Taubert K. Urbanization and Cardiovascular Disease: Raising Heart-Healthy Children in Today’s Cities. The World Heart Federation; Geneva, Switzerland: 2012.
-
- Lim S.S., Vos T., Flaxman A.D. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2224–2260. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials