Identification of Functional MKK3/6 and MEK1/2 Homologs from Echinococcus granulosus and Investigation of Protoscolecidal Activity of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Inhibitors In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 30348669
- PMCID: PMC6325220
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01043-18
Identification of Functional MKK3/6 and MEK1/2 Homologs from Echinococcus granulosus and Investigation of Protoscolecidal Activity of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Inhibitors In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
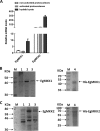
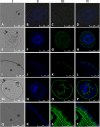
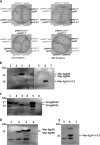
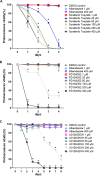
Cystic echinococcosis is a zoonosis caused by the larval stage of Echinococcus granulosussensu lato There is an urgent need to develop new drugs for the treatment of this disease. In this study, we identified two new members of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades, MKK3/6 and MEK1/2 homologs (termed EgMKK1 and EgMKK2, respectively), from E. granulosussensu stricto Both EgMKK1 and EgMKK2 were expressed at the larval stages. As shown by yeast two-hybrid and coimmunoprecipitation analyses, EgMKK1 interacted with the previously identified Egp38 protein but not with EgERK. EgMKK2, on the other hand, interacted with EgERK. In addition, EgMKK1 and EgMKK2 displayed kinase activity toward the substrate myelin basic protein. When sorafenib tosylate, PD184352, or U0126-ethanol (EtOH) was added to the medium for in vitro culture of E. granulosus protoscoleces (PSCs) or cysts, an inhibitory and cytolytic effect was observed via suppressed phosphorylation of EgMKKs and EgERK. Nonviability of PSCs treated with sorafenib tosylate or U0126-EtOH, and not with PD184352, was confirmed through bioassays, i.e., inoculation of treated and untreated protoscoleces into mice. In vivo treatment of E. granulosussensu stricto-infected mice with sorafenib tosylate or U0126-EtOH for 4 weeks demonstrated a reduction in parasite weight, but the results did not show a significant difference. In conclusion, the MAPK cascades were identified as new targets for drug development, and E. granulosus was efficiently inhibited by their inhibitors in vitro The translation of these findings into in vivo efficacy requires further adjustment of treatment regimens using sorafenib tosylate or, possibly, other kinase inhibitors.
Keywords: Echinococcus granulosus; MAPK kinases; chemotherapy; cystic echinococcosis; inhibitor.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis uncovers the key pathways and candidate genes related to the treatment of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces with the repurposed drug pyronaridine.BMC Genomics. 2021 Jul 13;22(1):534. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07875-w. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34256697 Free PMC article.
-
First Report of the Anti-Parasitic Effect of a Cannabis sativa full-spectrum Extract on Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto.Acta Parasitol. 2025 Jul 14;70(4):157. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01090-3. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40659847
-
Experimental cystic echinococcosis therapy: In vitro and in vivo combined 5-fluorouracil/albendazole treatment.Vet Parasitol. 2017 Oct 15;245:62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.08.011. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Vet Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28969840
-
Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes infecting humans--review of current knowledge.Int J Parasitol. 2014 Jan;44(1):9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24269720 Review.
-
A systematic review of medicinal plants used against Echinococcus granulosus.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 13;15(10):e0240456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240456. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33048959 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The evolution of TNF signaling in platyhelminths suggests the cooptation of TNF receptor in the host-parasite interplay.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Sep 25;13(1):491. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04370-1. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32977830 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Scolicidal Efficacy of 5-Fluorouracil and Radiation Against Protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus Sensu Lato.Acta Parasitol. 2022 Jun;67(2):820-826. doi: 10.1007/s11686-022-00518-4. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Acta Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35113338
-
An insight into pyocyanin: production, characterization, and evaluation of its in vitro antibacterial, antifungal, antibiofilm and in vivo anti-schistosomal potency.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Aug 23;25(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04248-1. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40847290 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Efficacies of the EGFR/MEK/ERK Signaling Inhibitors in the Treatment of Alveolar Echinococcosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Jul 22;64(8):e00341-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00341-20. Print 2020 Jul 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32482675 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Changes in the Global Transcriptome and MicroRNAome Reveal Complex miRNA-mRNA Regulation in Early Stages of the Bi-Directional Development of Echinococcus granulosus Protoscoleces.Front Microbiol. 2020 Apr 9;11:654. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00654. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32373094 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

