Spatiotemporal Loss of NF1 in Schwann Cell Lineage Leads to Different Types of Cutaneous Neurofibroma Susceptible to Modification by the Hippo Pathway
- PMID: 30348677
- PMCID: PMC6328325
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0151
Spatiotemporal Loss of NF1 in Schwann Cell Lineage Leads to Different Types of Cutaneous Neurofibroma Susceptible to Modification by the Hippo Pathway
Abstract
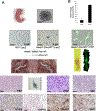
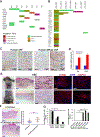
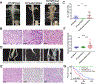
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a cancer predisposition disorder that results from inactivation of the tumor suppressor neurofibromin, a negative regulator of RAS signaling. Patients with NF1 present with a wide range of clinical manifestations, and the tumor with highest prevalence is cutaneous neurofibroma (cNF). Most patients harboring cNF suffer greatly from the burden of those tumors, which have no effective medical treatment. Ironically, none of the numerous NF1 mouse models developed so far recapitulate cNF. Here, we discovered that HOXB7 serves as a lineage marker to trace the developmental origin of cNF neoplastic cells. Ablating Nf1 in the HOXB7 lineage faithfully recapitulates both human cutaneous and plexiform neurofibroma. In addition, we discovered that modulation of the Hippo pathway acts as a "modifier" for neurofibroma tumorigenesis. This mouse model opens the doors for deciphering the evolution of cNF to identify effective therapies, where none exist today. SIGNIFICANCE: This study provides insights into the developmental origin of cNF, the most common tumor in NF1, and generates the first mouse model that faithfully recapitulates both human cutaneous and plexiform neurofibroma. The study also demonstrates that the Hippo pathway can modify neurofibromagenesis, suggesting that dampening the Hippo pathway could be an attractive therapeutic target.This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest
Figures


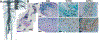
References
-
- Xu GF, O’Connell P, Viskochil D, Cawthon R, Robertson M, Culver M, Dunn D, Stevens J, Gesteland R, White R, et al. 1990. The neurofibromatosis type 1 gene encodes a protein related to GAP. Cell 62:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Ballester R, Marchuk D, Boguski M, Saulino A, Letcher R, Wigler M, and Collins F 1990. The NF1 locus encodes a protein functionally related to mammalian GAP and yeast IRA proteins. Cell 63:851–859. - PubMed
-
- Bajenaru ML, Hernandez MR, Perry A, Zhu Y, Parada LF, Garbow JR, and Gutmann DH 2003. Optic nerve glioma in mice requires astrocyte Nf1 gene inactivation and Nf1 brain heterozygosity. Cancer Res 63:8573–8577. - PubMed
-
- Lin AL, and Gutmann DH 2013. Advances in the treatment of neurofibromatosis-associated tumours. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10:616–624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

