Spleen Dose-Volume Parameters as a Predictor of Treatment-related Lymphopenia During Definitive Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer
- PMID: 30348711
- PMCID: PMC6365734
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.11409
Spleen Dose-Volume Parameters as a Predictor of Treatment-related Lymphopenia During Definitive Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal Cancer
Abstract
Aim: Our study sought to identify dosimetric predictors of treatment-related lymphopenia during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer.
Materials and methods: Patients with esophageal cancer who had received definitive chemoradiotherapy at our Institution were retrospectively assessed. The absolute volume of the spleen, body, and bone marrow that had received 5, 10, 20, and 30 Gy and the mean splenic dose were recorded.
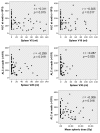
Results: Multivariate linear regression analysis revealed that docetaxel use and spleen dose-volume parameters (V5, V10, V20, V30, and mean splenic dose) were significant independent factors negatively influencing the absolute lymphocyte count at nadir. An increase of 1 Gy in mean splenic dose predicted a 2.9% decrease in nadir absolute lymphocyte count. Univariable logistic regression analysis showed that the mean splenic dose was a significant predictor of grade 4 lymphopenia. None of the body or bone marrow dose-volume parameters significantly predicted lymphopenia.
Conclusion: Higher spleen dose-volume parameters were associated with severe lymphopenia during chemoradiotherapy.
Keywords: Treatment-related lymphopenia; bone marrow; chemoradiotherapy; dose–volume parameters; spleen.
Copyright© 2018, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Does Unintentional Splenic Radiation Predict Outcomes After Pancreatic Cancer Radiation Therapy?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017 Feb 1;97(2):323-332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.046. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017. PMID: 28068240
-
Characterization and dosimetric predictors for absolute lymphocyte count changes during neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with or without pembrolizumab for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: an analysis of a prospective cohort.Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02581-9. Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39789555 Free PMC article.
-
Less Irradiation to Lymphocyte-Related Organs Reduced the Risk of G4 Lymphopenia in Esophageal Cancer: Re-Analysis of Prospective Trials.Oncologist. 2023 Aug 3;28(8):e645-e652. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyad109. Oncologist. 2023. PMID: 37285035 Free PMC article.
-
[Dosimetric factors related to postoperative pulmonary complications in locally advanced esophageal cancers treated with preoperative chemoradiotherapy: Literature review].Bull Cancer. 2020 Oct;107(10):982-990. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Bull Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32977935 Review. French.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of radiation-related lymphopenia on outcomes in pancreatic cancer.Future Oncol. 2022 May;18(15):1885-1895. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0483. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35132868
Cited by
-
Platelet-to-albumin ratio and radiation-induced lymphopenia-prognostic biomarker for carcinoma esophagus.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024 Feb 5;36(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s43046-024-00208-4. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024. PMID: 38311646
-
Severe Radiation-Induced Lymphopenia Affects the Outcomes of Esophageal Cancer: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;14(12):3024. doi: 10.3390/cancers14123024. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between splenic dose and radiation-induced lymphopenia.J Radiat Res. 2024 May 23;65(3):337-349. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrae023. J Radiat Res. 2024. PMID: 38718391 Free PMC article.
-
A review on lymphocyte radiosensitivity and its impact on radiotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 3;13:1201500. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1201500. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37601664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between unintentional splenic radiation and lymphopenia and high neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio after radiotherapy in patients with esophageal cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;10(12):5076-5084. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1765. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gu-Trantien C, Loi S, Garaud S, Equeter C, Libin M, de Wind A, Ravoet M, Le Buanec H, Sibille C, Manfouo-Foutsop G, Veys I, Haibe-Kains B, Singhal SK, Michiels S, Rothe F, Salgado R, Duvillier H, Ignatiadis M, Desmedt C, Bron D, Larsimont D, Piccart M, Sotiriou C, Willard-Gallo K. CD4(+) follicular helper T -cell infiltration predicts breast cancer survival. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:2873–2892. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shiraishi Y, Fang P, Xu C, Song J, Krishnan S, Koay EJ, Mehran RJ, Hofstetter WL, Blum-Murphy M, Ajani JA, Komaki R, Minsky B, Mohan R, Hsu CC, Hobbs BP, Lin SH. Severe lymphopenia during neoadjuvant chemoradiation for esophageal cancer: A propensity-matched analysis of the relative risk of proton versus photon-based radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol. 2017;128:154–160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wild AT, Ye X, Ellsworth SG, Smith JA, Narang AK, Garg T, Campian J, Laheru DA, Zheng L, Wolfgang CL, Tran PT, Grossman SA, Herman JM. The association between chemoradiation-related lymphopenia and clinical outcomes in patients with locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015;38:259–265. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical