Metabolic regulation of female puberty via hypothalamic AMPK-kisspeptin signaling
- PMID: 30348767
- PMCID: PMC6233121
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1802053115
Metabolic regulation of female puberty via hypothalamic AMPK-kisspeptin signaling
Abstract
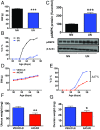
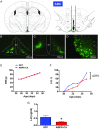
Conditions of metabolic distress, from malnutrition to obesity, impact, via as yet ill-defined mechanisms, the timing of puberty, whose alterations can hamper later cardiometabolic health and even life expectancy. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), the master cellular energy sensor activated in conditions of energy insufficiency, has a major central role in whole-body energy homeostasis. However, whether brain AMPK metabolically modulates puberty onset remains unknown. We report here that central AMPK interplays with the puberty-activating gene, Kiss1, to control puberty onset. Pubertal subnutrition, which delayed puberty, enhanced hypothalamic pAMPK levels, while activation of brain AMPK in immature female rats substantially deferred puberty. Virogenetic overexpression of a constitutively active form of AMPK, selectively in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC), which holds a key population of Kiss1 neurons, partially delayed puberty onset and reduced luteinizing hormone levels. ARC Kiss1 neurons were found to express pAMPK, and activation of AMPK reduced ARC Kiss1 expression. The physiological relevance of this pathway was attested by conditional ablation of the AMPKα1 subunit in Kiss1 cells, which largely prevented the delay in puberty onset caused by chronic subnutrition. Our data demonstrate that hypothalamic AMPK signaling plays a key role in the metabolic control of puberty, acting via a repressive modulation of ARC Kiss1 neurons in conditions of negative energy balance.
Keywords: AMPK; Kiss1; energy balance; puberty; undernutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Waterson MJ, Horvath TL. Neuronal regulation of energy homeostasis: Beyond the hypothalamus and feeding. Cell Metab. 2015;22:962–970. - PubMed
-
- Parent AS, et al. The timing of normal puberty and the age limits of sexual precocity: Variations around the world, secular trends, and changes after migration. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:668–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

