A multi-tissue full lifespan epigenetic clock for mice
- PMID: 30348905
- PMCID: PMC6224226
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.101590
A multi-tissue full lifespan epigenetic clock for mice
Abstract
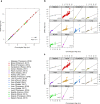
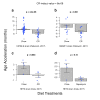
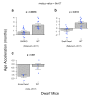
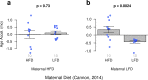
Human DNA-methylation data have been used to develop highly accurate biomarkers of aging ("epigenetic clocks"). Recent studies demonstrate that similar epigenetic clocks for mice (Mus Musculus) can be slowed by gold standard anti-aging interventions such as calorie restriction and growth hormone receptor knock-outs. Using DNA methylation data from previous publications with data collected in house for a total 1189 samples spanning 193,651 CpG sites, we developed 4 novel epigenetic clocks by choosing different regression models (elastic net- versus ridge regression) and by considering different sets of CpGs (all CpGs vs highly conserved CpGs). We demonstrate that accurate age estimators can be built on the basis of highly conserved CpGs. However, the most accurate clock results from applying elastic net regression to all CpGs. While the anti-aging effect of calorie restriction could be detected with all types of epigenetic clocks, only ridge regression based clocks replicated the finding of slow epigenetic aging effects in dwarf mice. Overall, this study demonstrates that there are trade-offs when it comes to epigenetic clocks in mice. Highly accurate clocks might not be optimal for detecting the beneficial effects of anti-aging interventions.
Keywords: DNA methylation; biological age; epigenetic clock; mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Christensen BC, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ, Zheng S, Wrensch MR, Wiemels JL, Nelson HH, Karagas MR, Padbury JF, Bueno R, Sugarbaker DJ, Yeh RF, Wiencke JK, Kelsey KT. Aging and environmental exposures alter tissue-specific DNA methylation dependent upon CpG island context. PLoS Genet. 2009; 5:e1000602. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000602 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rakyan VK, Down TA, Maslau S, Andrew T, Yang TP, Beyan H, Whittaker P, McCann OT, Finer S, Valdes AM, Leslie RD, Deloukas P, Spector TD. Human aging-associated DNA hypermethylation occurs preferentially at bivalent chromatin domains. Genome Res. 2010; 20:434–39. 10.1101/gr.103101.109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Teschendorff AE, Menon U, Gentry-Maharaj A, Ramus SJ, Weisenberger DJ, Shen H, Campan M, Noushmehr H, Bell CG, Maxwell AP, Savage DA, Mueller-Holzner E, Marth C, et al.. Age-dependent DNA methylation of genes that are suppressed in stem cells is a hallmark of cancer. Genome Res. 2010; 20:440–46. 10.1101/gr.103606.109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

