Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations
- PMID: 30348985
- PMCID: PMC6197289
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06318-7
Single cell RNA sequencing of human liver reveals distinct intrahepatic macrophage populations
Abstract
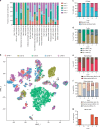
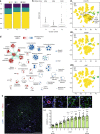
The liver is the largest solid organ in the body and is critical for metabolic and immune functions. However, little is known about the cells that make up the human liver and its immune microenvironment. Here we report a map of the cellular landscape of the human liver using single-cell RNA sequencing. We provide the transcriptional profiles of 8444 parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells obtained from the fractionation of fresh hepatic tissue from five human livers. Using gene expression patterns, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemical examinations, we identify 20 discrete cell populations of hepatocytes, endothelial cells, cholangiocytes, hepatic stellate cells, B cells, conventional and non-conventional T cells, NK-like cells, and distinct intrahepatic monocyte/macrophage populations. Together, our study presents a comprehensive view of the human liver at single-cell resolution that outlines the characteristics of resident cells in the liver, and in particular provides a map of the human hepatic immune microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Transcriptomic Traces of Adult Human Liver Progenitor Cells.Hepatology. 2020 Apr;71(4):1504-1507. doi: 10.1002/hep.31143. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31991483 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

