Drug delivery systems for elemene, its main active ingredient β-elemene, and its derivatives in cancer therapy
- PMID: 30349250
- PMCID: PMC6186893
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S174527
Drug delivery systems for elemene, its main active ingredient β-elemene, and its derivatives in cancer therapy
Abstract
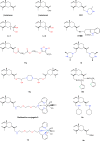
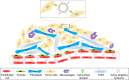
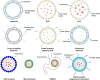
β-elemene is a noncytotoxic Class II antitumor drug extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Curcuma wenyujin Y. H. Chen et C. Ling. β-elemene exerts its effects by inhibiting cell proliferation, arresting the cell cycle, inducing cell apoptosis, exerting antiangiogenesis and antimetastasis effects, reversing multiple-drug resistance (MDR), and enhancing the immune system. Elemene injection and oral emulsion have been used to treat various tumors, including cancer of the lung, liver, brain, breast, ovary, gastric, prostate, and other tissues, for >20 years. The safety of both elemene injection and oral emulsion in the clinic has been discussed. Recently, the secondary development of β-elemene has attracted the attention of researchers and made great progress. On the one hand, studies have been carried out on liposome-based systems (including solid lipid nanoparticles [SLNs], nanostructured lipid carriers [NLCs], long-circulating liposomes, active targeting liposomes, and multidrug-loaded liposomes) and emulsion systems (including microemulsions, self-emulsion drug delivery systems [SEDDSs], and active targeting microemulsion) to solve the issues of poor solubility in water, low bioavailability, and severe phlebitis, as well as to improve antitumor efficacy. The pharmacokinetics of different drug delivery systems of β-elemene are also summarized. On the other hand, a number of highly active anticancer β-elemene derivatives have been obtained through modification of the structure of β-elemene. This review focuses on the two drug delivery systems and derivatives of β-elemene for cancer therapy.
Keywords: derivative; drug delivery system; pharmacokinetics; safety; β-elemene.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applications of nanoparticles in herbal medicine: zedoary turmeric oil and its active compound β-elemene.Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(6):1093-102. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X11009421. Am J Chin Med. 2011. PMID: 22083983 Review.
-
Preparation, characterization, pharmacokinetics and anticancer effects of PEGylated β-elemene liposomes.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Feb 15;17(1):60-75. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0156. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32296587 Free PMC article.
-
The Preparation, Determination of a Flexible Complex Liposome Co-Loaded with Cabazitaxel and β-Elemene, and Animal Pharmacodynamics on Paclitaxel-Resistant Lung Adenocarcinoma.Molecules. 2019 Apr 30;24(9):1697. doi: 10.3390/molecules24091697. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31052317 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and characterization of β-elemene-loaded microemulsion.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011 Jul;37(7):765-74. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2010.541261. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011. PMID: 21244276
-
Anti-Tumor Drug Discovery Based on Natural Product β-Elemene: Anti-Tumor Mechanisms and Structural Modification.Molecules. 2021 Mar 10;26(6):1499. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061499. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33801899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of Chinese and Western Medicine to Prevent and Reverse Resistance of Cancer Cells to Anticancer Drugs.Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Apr;26(4):251-255. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3180-x. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 31705451
-
The function of natural compounds in important anticancer mechanisms.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1049888. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1049888. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-elemene suppresses tumor metabolism and stem cell-like properties of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 15;12(4):1535-1555. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35530288 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt-dependent and Wnt-independent functions of BCL9 in development, tumorigenesis, and immunity: Implications in therapeutic opportunities.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 11;11(2):701-710. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.012. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Understanding the Mechanisms of Elemene in Reversing Drug Resistance in Tumor Cells: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Sep 24;26(19):5792. doi: 10.3390/molecules26195792. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tang CY, Zhu LX, Yu JD, et al. Effect of β-elemene on the kinetics of intracellular transport of d-luciferin potassium salt (ABC substrate) in doxorubicin-resistant breast cancer cells and the associated molecular mechanism. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;120:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Yu X, Xu M, Li N, et al. β-elemene inhibits tumor-promoting effect of M2 macrophages in lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;490(2):514–520. - PubMed
-
- Guo Z, Liu Z, Yue H, Wang J. Beta-elemene increases chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil through down-regulating microRNA-191 expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):7032–7039. - PubMed
-
- Zhu TZ, Li XM, Luo LH, et al. β-elemene inhibits stemness, promotes differentiation and impairs chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma stem-like cells. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(2):699–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

