Clinical significance and biological roles of cyclins in gastric cancer
- PMID: 30349301
- PMCID: PMC6186297
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S171716
Clinical significance and biological roles of cyclins in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background and aim: Cyclins have been reported to be overexpressed with poor prognosis in several human cancers. However, limited numbers of studies evaluated the expressions and prognostic roles of cyclins in gastric cancer (GC). We aim to evaluate the expressions and prognostic roles of cyclins. Also, further efforts were made to explore biological function of the differentially expressed cyclins.
Methods: Cyclins expressions were analyzed by Oncomine and The Cancer Genome Atlas datasets, and the prognostic roles of cyclins in GC patients were investigated by the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database. Then, a comprehensive PubMed literature search was performed to identify expression and prognosis of cyclins in GC. Biological functions of the differentially expressed cyclins were explored through Enrich R platform, and KEGG and transcription factor were analyzed.
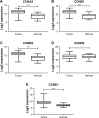
Results: The expression levels of CCNA2 (cyclin A2), CCNB1 (cyclin B1), CCNB2 (cyclin B2), and CCNE1 (cyclin E1) mRNAs were identified to be significantly higher in GC tissues than in normal tissues in both Oncomine and The Cancer Genome Atlas datasets. High expressions of CCNA2, CCNB1, and CCNB2 mRNAs were identified to be related with poor overall survival in Kaplan-Meier Plotter dataset. Evidence from clinical studies showed that CCNB1 was related with overall survival in GC patients. Cyclins were associated with several biological pathways, including cell cycle, p53 signaling pathway, FoxO signaling pathway, viral carcinogenesis, and AMPK signaling pathway. Enrichment analysis also showed that cyclins interacted with some certain transcription factors, such as FOXM1, SIN3A, NFYA, and E2F4.
Conclusion: Based on our results, high expressions of cyclins were related with poor prognosis in GC patients. The above information might be useful for better understanding the clinical and biological roles of cyclins mRNA and guiding individualized treatments for GC patients.
Keywords: biological function; cyclins; expression; gastric cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Upregulated cyclins may be novel genes for triple-negative breast cancer based on bioinformatic analysis.Breast Cancer. 2020 Sep;27(5):903-911. doi: 10.1007/s12282-020-01086-z. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32338339
-
Bioinformatical Analysis of Gene Expression Omnibus Database Associates TAF7/CCNB1, TAF7/CCNA2, and GTF2E2/CDC20 Pathways with Glioblastoma Development and Prognosis.World Neurosurg. 2020 Jun;138:e492-e514. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.02.159. Epub 2020 Mar 5. World Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32147549
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Cyclin Family Gene Expression in Colon Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 29;11:674394. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.674394. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33996604 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions and prognostic values of the E2F transcription factors in human breast carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Sep 13;10:3521-3532. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S172332. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30271201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E- and A-type cyclins as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003 Sep;3(5):617-33. doi: 10.1586/14737159.3.5.617. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2003. PMID: 14510182 Review.
Cited by
-
pH-Responsive PEGylated Niosomal Nanoparticles as an Active-Targeting Cyclophosphamide Delivery System for Gastric Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2022 Aug 24;27(17):5418. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175418. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080186 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic alterations of cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of gastric cancer.J Transl Med. 2023 May 2;21(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04077-8. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37131253 Free PMC article.
-
Bruceine D inhibits Cell Proliferation Through Downregulating LINC01667/MicroRNA-138-5p/Cyclin E1 Axis in Gastric Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 24;11:584960. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584960. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33390953 Free PMC article.
-
Four Novel Prognostic Genes Related to Prostate Cancer Identified Using Co-expression Structure Network Analysis.Front Genet. 2021 Apr 1;12:584164. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.584164. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33927744 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Potential Therapeutic Target for E2F1 and Prognostic Factors of E2F1/2/3/5/7/8 in Human Gastric Cancer.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020 Jul 31;18:824-838. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.07.017. eCollection 2020 Sep 11. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020. PMID: 32953933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–2917. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

