Role of monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting sorafenib response in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30349306
- PMCID: PMC6188073
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S173275
Role of monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in predicting sorafenib response in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Sorafenib is the first-line treatment for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and its clinical response rate is only about 10%. In clinical practice, some HCC patients obtain favorable overall survival (OS) to the treatment of sorafenib while some patients do not demonstrate a sensitive response to sorafenib. Therefore, it is valuable to determine the subgroups of patients who respond well as well as poorly to sorafenib. Thus, clinical variables of advanced HCC patients with sorafenib treatment were compiled to investigate whether monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) could be a biomarker for predicting sorafenib response.
Patients and methods: In this study, a total of 142 patients with advanced HCC were enrolled from January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2016 at the Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. MLR was analyzed using a ROC curve. A Cox regression model and log-rank test were performed to analyze the relationship between clinical factors and OS, as well as progression free survival (PFS).
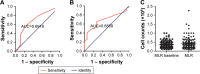
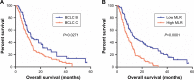
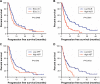
Results: The optimal cut-off point for MLR was 0.35, and MLR level had no significant correlation with age, gender, hepatitis B infection, grade, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level and state of portal vein tumor thrombus. Multivariate Cox regression model showed that grade (HR: 0.608, 95% CI: 0.409-0.904, P=0.014), AFP (HR: 0.445, 95% CI: 0.307-0.645, P=0.0001), MLR (HR: 0.445, 95% CI: 0.301-0.658, P=0.0001) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (HR: 1.005, 95% CI: 1.001-1.009, P=0.007) may serve as independent prognostic predictors for OS, and MLR maintained significant correlation with PFS in HCC patients (HR: 0.457, 95% CI: 0.308-0.678, P=0.0001). By log-rank test, there was longer PFS and OS in patients with low MLR than in those with high MLR (both P=0.0001).
Conclusion: MLR can predict sorafenib response and a high MLR is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with advanced HCC.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Predictive role of the monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jan;11(1):160-170. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1760. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35261893 Free PMC article.
-
Liver stiffness in magnetic resonance elastography is prognostic for sorafenib-treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2021 Apr;31(4):2507-2517. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07357-9. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33033862
-
Efficacy and safety of sequential therapy with sorafenib and regorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a two-center study in China.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(3):1266-1277. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-397. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837206 Free PMC article.
-
On-Treatment Albumin-Bilirubin Grade: Predictor of Response and Outcome of Sorafenib-Regorafenib Sequential Therapy in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 26;13(15):3758. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153758. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359658 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy versus sorafenib in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Aug;35(8):1277-1287. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15010. Epub 2020 Mar 3. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32052876
Cited by
-
Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio-based nomogram for predicting outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib.Hepatol Int. 2020 Sep;14(5):776-787. doi: 10.1007/s12072-020-10076-4. Epub 2020 Aug 1. Hepatol Int. 2020. PMID: 32740886 Free PMC article.
-
Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in peripheral whole blood samples of colorectal cancer patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 21;26(31):4639-4655. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i31.4639. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32884222 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological Aspects and Inflammation-Immune Markers in Alcohol and/or Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated With Sorafenib.Gastroenterology Res. 2024 Feb;17(1):23-31. doi: 10.14740/gr1689. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Gastroenterology Res. 2024. PMID: 38463146 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an inflammatory response-related signature in triple negative breast cancer for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 15;13:1175000. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1175000. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37397391 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammation Response Index is a Prognostic Risk Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Undergoing TACE.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021 Jun 21;14:2589-2600. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S316740. eCollection 2021. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021. PMID: 34188570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-Based Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(4):835–853. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–390. - PubMed
-
- Wörns MA, Galle PR. HCC therapies – lessons learned. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11(7):447–452. - PubMed
-
- Berasain C. Hepatocellular carcinoma and sorafenib: too many resistance mechanisms? Gut. 2013;62(12):1674–1675. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

